Editor’s note: This is the seventh of twelve lectures by Charles Kingsley, published as The Roman and the Teuton (1889).
(Go back to Lecture VI: The Nemesis of the Goths)
LECTURE VII: PAULUS DIACONUS
And now I come to the final settlement of Italy and the Lombard race; and to do that well, I must introduce you today to an old chronicler—a very valuable, and as far as we know, faithful writer—Paul Warnefrid, alias Paul the Deacon.
I shall not trouble you with much commentary on him; but let him, as much as possible, tell his own story. He may not be always quite accurate, but you will get no one more accurate. In the long run, you will know nothing about the matter, save what he tells you; so be content with what you can get. Let him shew you what sort of an account of his nation, and the world in general, a Lombard gentleman and clergyman could give, at the end of the 8th century.
You recollect the Lombards, of whom Tacitus says, ‘Longobardos paucitas nobilitat.’ Paulus Warnefrid was one of their descendants, and his history carries out the exact truth of Tacitus’ words. He too speaks of them as a very small tribe. He could not foresee how much the ‘nobilitat’ meant. He knew his folk as a brave semi-feudal race, who had conquered the greater part of Italy, and tilled and ruled it well; who were now conquered by Charlemagne, and annexed to the great Frank Empire, but without losing anything of their distinctive national character. He did not foresee that they would become the architects, the merchants, the goldsmiths, the bankers, the scientific agriculturists of all Europe. We know it. Whenever in London or any other great city, you see a ‘Lombard Street,’ an old street of goldsmiths and bankers—or the three golden balls of Lombardy over a pawnbroker’s shop—or in the country a field of rye-grass, or a patch of lucerne—recollect this wise and noble people, and thank the Lombards for what they have done for mankind.
Paulus is a garrulous historian, but a valuable one, just because he is garrulous. Though he turned monk and deacon in middle life, he has not sunk the man in the monk, and become a cosmopolite, like most Roman ecclesiastics, who have no love or hate for human beings save as they are friends or enemies of the pope, or their own abbey. He has retained enough of the Lombard gentleman to be proud of his family, his country, and the old legends of his race, which he tells, half-ashamed, but with evident enjoyment.
He was born at beautiful Friuli, with the jagged snow-line of the Alps behind him, and before him the sun and the sea, and the plains of Po; he was a courtier as a boy in Desiderius’ court at Pavia, and then, when Charlemagne destroyed the Lombard monarchy, seems to have been much with the great king at Aix. He certainly ended his life as a Benedictine monk, at Monte Casino, about 799; having written a Life of St. Gregory; Homilies long and many; the Appendix to Eutropius (the Historia Miscella, as it is usually called) up to Justinian’s time; and above all, this history of the Lombards, his forefathers, which I shall take as my text.
To me, and I believe to the great German antiquaries, his history seems a model history of a nation. You watch the people and their story rise before you out of fable into fact; out of the dreary darkness of the unknown north, into the clear light of civilized Roman history.
The first chapter is ‘Of Germany, how it nourishes much people, and therefore many nations go forth of it.’ The reason which he gives for the immense population is significant. The further to the north, and the colder, the more healthy he considers the world to be, and more fit for breeding human beings; whereas the south, being nearer to the heat of the sun, always abounds with diseases. The fact really is, I presume, that Italy (all the south which he knew), and perhaps most of the once Roman empire, were during the 6th and 7th centuries pestilential. Ruined cities, stopt watercourses, cultivated land falling back into marsh and desert, a soil too often saturated with human corpses—offered all the elements for pestilence. If the once populous Campagna of Rome be now uninhabitable from malaria, what must it have been in Paul Warnefrid’s time?
Be that as it may, this is his theory.
Then he tells us how his people were at first called Winils; and how they came out of Scania Insula. Sweden is often, naturally, an island with the early chroniclers; only the south was known to them. The north was magical, unknown, Quenland, the dwelling-place of Yotuns, Elves, Trolls, Scratlings, and all other uncanny inhumanities. The Winils find that they are growing too many for Scanland, and they divide into three parties. Two shall stay behind, and the third go out to seek their fortunes. Which shall go is to be decided by lot. The third on whom the lot falls choose as war-kings, two brothers, Ayo and Ibor, and with them their mother, Gambara, the Alruna-wife, prudent and wise exceedingly—and they go forth.
But before Paul can go too, he has a thing or two to say, which he must not forget, about the wild mysterious north from which his forefathers came. First how, in those very extreme parts of Germany, in a cave on the ocean shore, lie the seven sleepers. How they got thither from Ephesus, I cannot tell, still less how they should be at once there on the Baltic shore, and at Ephesus—as Mohammed himself believed, and Edward the Confessor taught—and at Marmoutier by Tours, and probably elsewhere beside. Be that as it may, there they are, the seven martyrs, sleeping for ever in their Roman dresses, which some wild fellow tried to pull off once, and had his arms withered as a punishment. And Paul trusts that they will awake some day, and by their preaching save the souls of the heathen Wends and Finns who haunt those parts.
The Teutonic knights, however, and not the seven sleepers, did that good work.
Only their dog is not with them, it appears;—the sacred dog which watches them till the judgment day, when it is to go up to heaven, with Noah’s dove, and Balaam’s ass, and Alborah the camel, and all the holy beasts. The dog must have been left behind at Ephesus.
Then he must tell us about the Scritofinns of the Bothnia gulf; wild Lapps and Finns, who have now retreated before the Teutonic race. In Paul Warnefrid’s eyes they are little wild hopping creatures—whence they derive their name, he says—Scritofinns, the hopping, or scrambling Finns.
Scrattels, Skretles, often figure in the Norse tales as hopping dwarfs, half magical. The Norse discoverers of America recognized the Skrællings in the Esquimaux, and fled from them in panic terror; till that furious virago Freydisa, Thorvard’s wife, and Eirek the Red’s daughter, caught up a dead man’s sword, and put to flight, single-handed, the legion of little imps.
Others, wiser, or too wise, say that Paul is wrong; that Skrikfins is the right name, so called from their ‘screeking’, screaming, and jabbering, which doubtless the little fellows did, loudly enough.
Be that as it may, they appear to Paul (or rather to his informants, Wendish merchants probably, who came down to Charlemagne’s court at Aix, to sell their amber and their furs) as hopping about, he says, after the rein-deer, shooting them with a little clumsy bow, and arrows tipt with bone, and dressing themselves in their skins. Procopius knew these Scritfins too (but he has got (as usual) addled in his geography, and puts them in ultima Thule or Shetland), and tells us, over and above the reindeer-skin dresses, that the women never nursed their children, but went out hunting with their husbands, hanging the papoose up to a tree, as the Lapps do now, with a piece of deer’s marrow in its mouth to keep it employed; and moreover, that they sacrificed their captives to a war-god (Mars he calls him) in cruel ugly ways. All which we may fully believe.
Then Paul has to tell us how in the Scritfin country there is little or no night in midsummer, little or no day in winter; and how the shadows there are exceeding long, and shorten to nothing as they reach the equator,—where he puts not merely Egypt, but Jerusalem. And how on Christmas days a man’s shadow is nine feet long in Italy, whereas at Totonis Villam (Thionville), as he himself has measured, it is nineteen feet and a half. Because, he says, shrewdly enough, the further you go from the sun, the nearer the sun seems to the horizon. Of all which if you answer—But this is not history: I shall reply—But it is better than history. It is the history of history. It helps you to see how the world got gradually known; how history got gradually to be written; how each man, in each age, added his little grain to the great heap of facts, and gave his rough explanation thereof; and how each man’s outlook upon this wondrous world grew wider, clearer, juster, as the years rolled on.
And therefore I have no objection at all to listen to Paul in his next chapter, concerning the two navels of the ocean, one on each side Britain—abysses which swallow up the water twice a day, and twice a day spout it up again. Paul has seen, so he seems to say, the tide, the ’Ωκεανοιο ροας, that inexplicable wonder of the old Greeks and Romans, running up far inland at the mouths of the Seine and Loire; and he has to get it explained somehow, before he can go forward with a clear conscience. One of the navels seems to be the Mahlstrom in Norway. Of the place of the other there is no doubt. It is close to Evodia insula, seemingly Alderney. For a high noble of the French told him so; he was sucked into it, ships and all, and only escaped by clinging to a rock. And after awhile the margins of that abyss were all left bare, leaving the Frenchman high and dry, ‘palpitating so with fear,’ says Paul, ‘that he could hardly keep his seat.’ But when all the water had been sucked in, out and up it came pouring again, in huge mountains, and upon them the Frenchman’s ships, to his intense astonishment, reappeared out of the bottomless pit; into one of which he jumped; being, like a true Frenchman, thoroughly master of the situation; and got safe home to tell Paul the deacon. It is not quite the explanation of the tides which one would have wished for: but if a French nobleman of high rank will swear that he saw it with his own eyes, what can Paul do, in common courtesy, but believe him?
Paul has observed, too, which is a fact, that there is a small tide in his own Adriatic; and suggests modestly that there may be a similar hole in the bottom of that sea, only a little one, the tide being very little. After which, ‘his prælibatis,’ he will return, he says, to his story. And so he goes back to the famous Langbard Saga, the old story, which he has turned out of living Teutonic verse into dead Latin prose, and calls De Woden et Frea quædam ridicula fabula; but can’t help for the life of him telling it, apologizing all the time. How the Winils (his own folk) went out to fight the Wendels, many more than them in number; and how Gambara, the Alruna-wife, cried to Freia the goddess, and Freia told her that whichsoever of the two armies first greeted Woden at the sunrise should win. But the Winils are far away on the war-road, and there is no time to send to them. So Freia bids her take the Winil women, and dress them as warriors, and plait their tresses over their lips for beards, and cry to Woden; and Woden admires their long beards, and thinks them such valiant ‘war-beasts,’ that he grants them the victory.
Then Freia tells him how he has been taken in, and the old god laughs till the clouds rattle again, and the Winils are called Langbardr ever after.
But then comes in the antiquary, and says that the etymology is worthless, and that Langbardr means long axes—(bard=an axe)—a word which we keep in halbert, a hall-axe, or guard’s pole-axe; and perhaps the antiquary is right.
But again comes in a very learned man, Dr. Latham, and more than hints that the name is derived from the Lange Börde, the long meadows by the side of the Elbe: and so a good story crumbles to pieces, and
‘All charms do fly
Beneath the touch of cold philosophy.’
Then follows another story, possibly from another saga. How by reason of a great famine they had to leave Scoringia, the shore-land, and go into Mauringia, a word which Mr. Latham connects with the Merovingi, or Meerwing conquerors of Gaul. Others say that it means the moorland, others something else. All that they will ever find out we may see for ourselves already.—A little tribe of valiant fair-haired men, whether all Teutons, or, as Mr. Latham thinks, Sclavonians with Teuton leaders, still intimately connected with our own English race both by their language and their laws, struggling for existence on the bleak brown bogs and moors, sowing a little barley and flax, feeding a few rough cattle, breeding a few great black horses; generation after generation fighting their way southward, as they exhausted the barren northern soils, or became too numerous for their marches, or found land left waste in front of them by the emigration of some Suevic, Vandal, or Burgund tribe. We know nothing about them, and never shall know, save that they wore white linen gaiters, and carried long halberts, or pole-axes, and had each an immortal soul in him, as dear to God as yours or mine, with immense unconscious capabilities, which their children have proved right well.
Then comes another saga, how they met the Assipitti, of whom, whether they were Tacitus’s Usipetes, of the Lower Rhine, or Asabiden, the remnant of the Asen, who went not to Scandinavia with Odin, we know not, and need not know; and how the Assipitti would not let them pass; and how they told the Lombards that they had dogheaded men in their tribe who drank men’s blood, which Mr. Latham well explains by pointing out, in the Traveller’s Song, a tribe of Hundings (Houndings) sons of the hound; and how the Lombards sent out a champion, who fought the champion of the Assipitti, and so gained leave to go on their way.
Forward they go, toward the south-east, seemingly along the German marches, the debateable land between Teuton and Sclav, which would, mechanically speaking, be the line of least resistance. We hear of Gothland—wherever that happened to be just then; of Anthaib, the land held by the Sclavonian Anten, and Bathaib, possibly the land held by the Gepidæ, or remnant of the Goths who bided behind (as Wessex men still say), while the Goths moved forward; and then of Burgundhaib, wherever the Burgunds might be then. I know not; and I will dare to say, no man can exactly know. For no dates are given, and how can they be? The Lombards have not yet emerged out of the dismal darkness of the north into the light of Roman civilization; and all the history they have are a few scraps of saga.
At last they take a king of the family of the Gungings, Agilmund, son of Ayo, like the rest of the nations, says Jornandes; for they will be no more under duces, elective war-kings. And then follows a fresh saga (which repeats itself in the myths of several nations), how a woman has seven children at a birth, and throws them for shame into a pond; and Agilmund the king, riding by, stops to see, and turns them over with his lance; and one of the babes lays hold thereof; and the king says, ‘This will be a great man;’ and takes him out of the pond, and calls him Lamissohn, ‘the son of the fishpond,’ (so it is interpreted;) who grows to be a mighty Kemper-man, and slays an Amazon. For when they come to a certain river, the Amazons forbid them to pass, unless they will fight their she-champion; and Lamissohn swims over and fights the war-maiden, and slays her; and they go on and come into a large land and quiet, somewhere about Silesia, it would seem, and abode there a long while.
Then down on them come the savage Bulgars by night, and slay king Agilmund, and carry off his daughter; and Lamissohn follows them, and defeats them with a great slaughter, and is made king; and so forth: till at last they have got—how we shall never know—near history and historic lands. For when Odoacer and his Turklings and other confederates went up into Rugiland, the country north of Vienna, and destroyed the Rugians, and Fava their king, then the Lombards went down into the waste land of the Rugians, because it was fertile, and abode there certain years.
Then they moved on again, we know not why, and dwelt in the open plains, which are called feld. One says ‘Moravia;’ but that they had surely left behind. Rather it is the western plain of Hungary about Comorn. Be that as it may, they quarrelled there with the Heruli. Eutropius says that they paid the Herules tribute for the land, and offered to pay more, if the Herules would not attack them. Paul tells a wild saga, or story, of the Lombard king’s daughter insulting a Herule prince, because he was short of stature: he answered by some counter-insult; and she, furious, had him stabbed from behind through a window as he sat with his back to it. Then war came. The Herules, old and practised warriors, trained in the Roman armies, despised the wild Lombards, and disdained to use armour against them, fighting with no clothes save girdles. Rodulf their king, too certain of victory, sat playing at tables, and sent a man up a tree to see how the fight went, telling him that he would cut his head off if he said that the Herules fled; and then, touched by some secret anxiety as to the end, spoke the fatal words himself; and a madness from God came on the Herules; and when they came to a field of flax, they took the blue flowers for water, and spread out their arms to swim through, and were all slaughtered defencelessly.
Then they fought with the Suevi; and their kings’ daughters married with the kings of the Franks; and then ruled Aldwin (a name which Dr. Latham identifies with our English Eadwin, or Edwin, ‘the noble conqueror,’ though Grotius translates it Audwin, ‘the old or auld conqueror’), who brought them over the Danube into Pannonia, between the Danube and the Drave, about the year 526. Procopius says, that they came by a grant from the Emperor Justinian, who gave as wife to Aldwin a great niece of Dietrich the Good, carried captive with Witigis to Byzant.
Thus at last they too have reached the forecourt of the Roman Empire, and are waiting for their turn at the Nibelungen hoard. They have one more struggle, the most terrible of all; and then they will be for a while the most important people of the then world.
The Gepidæ are in Hungary before them, now a great people. Ever since they helped to beat the Huns at Netad, they have been holding Attila’s old kingdom for themselves and not attempting to move southward into the Empire; so fulfilling their name.
There is continual desultory war; Justinian, according to Procopius’ account, playing false with each, in order to make them destroy each other. Then, once (this is Procopius’ story, not Paul’s) they meet for a great fight; and both armies run away by a panic terror; and Aldwin the Lombard and Thorisend the Gepid are left alone, face to face.—It is the hand of God, say the two wild kings—God does not mean these two peoples to destroy each other. So they make a truce for two years. Then the Gepidæ call in Cutuguri, a Hunnic tribe, to help them; then, says Procopius, Aldwin, helped by Roman mercenaries, under Amalfrid the Goth, Theodoric’s great nephew, and brother-in-law of Aldwin, has a great fight with the Gepidæ. But Paul knows naught of all this: with him it is not Aldwin, but Alboin his son, who destroys the Gepidæ. Alboin, Grotius translates as Albe-win, ‘he who wins all:’ but Dr. Latham, true to his opinion that the Lombards and the Angles were closely connected, identifies it with our Ælfwine, ‘the fairy conqueror.’
Aldwin, Paul says, and Thorisend fought in the Asfeld,—wherever that may be,—and Alboin the Lombard prince slew Thorisend the Gepid prince, and the Gepidæ were defeated with a great slaughter.
Then young Alboin asked his father to let him sit at the table with him. No, he could not do that, by Lombard custom, till he has become son-at-arms to some neighbouring king.
Young Alboin takes forty thanes, and goes off to Thorisend’s court, as the guest of his enemy. The rites of hospitality are sacred. The king receives him, feasts him, seats him, the slayer of his son, in his dead son’s place. And as he looks on him he sighs; and at last he can contain no longer. The seat, he says, I like right well: but not the man who sits in it. One of his sons takes fire, and begins to insult the Lombards and their white gaiters. You Lombards have white legs like so many brood mares. A Lombard flashes up. Go to the Asfeld, and you will see how Lombard mares can kick. Your brother’s bones are lying about there like any sorry nag’s. This is too much; swords are drawn; but old Thorisend leaps up. He will punish the first man who strikes. Guests are sacred. Let them sit down again, and drink their liquor in peace. And after they have drunk, he gives Alboin his dead son’s weapons, and lets them go in peace, like a noble gentleman.
This grand old King dies in peace. Aldwin dies likewise, and to them succeed their sons, Alboin and Cunimund—the latter probably the prince who made the jest about the brood-mares—and they two will fight the quarrel out. Cunimund, says Paul, began the war—of course that is his story. Alboin is growing a great man; he has married a daughter of Clotaire, king of the Franks: and now he takes to his alliance the Avars, who have just burst into the Empire, wild people who afterwards founded a great kingdom in the Danube lands, and they ravage Cunimund’s lands. He will fight the Lombards first, nevertheless: he can settle the Avars after. He and his, says Paul, are slain to a man. Alboin makes a drinking-cup of his skull, carries off his daughter Rosamund (‘Rosy-mouth’), and a vast multitude of captives and immense wealth. The Gepidæ vanish from history; to this day (says Paul) slaves either of the Lombards or the Huns (by whom he rather means Avars); and Alboin becomes the hero of his time, praised even to Paul’s days in sagas, Saxon and Bavarian as well as Lombard, for his liberality and his glory. We shall see now how he has his chance at the Nibelungen hoard.
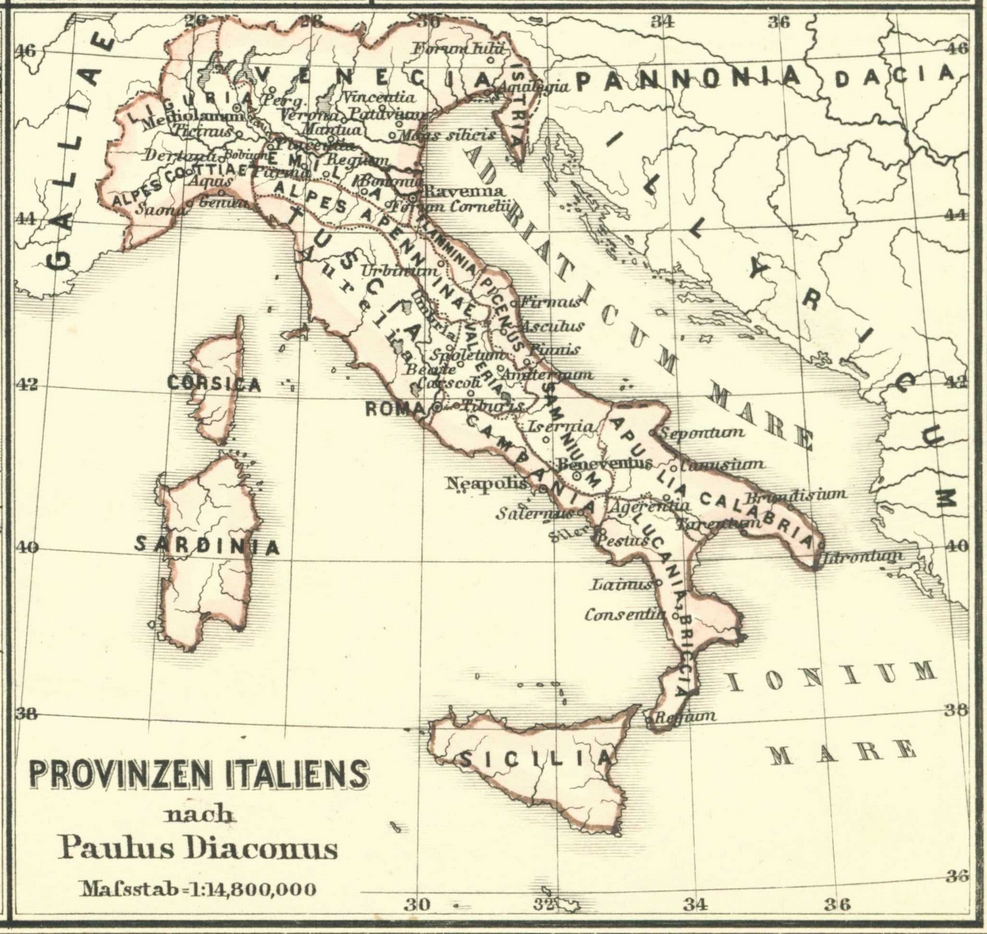
He has heard enough (as all Teutons have) of Italy, its beauty, and its weakness. He has sent five thousand chosen warriors to Narses, to help him against Totila and the Ostrogoths; and they have told him of the fair land and large, with its vineyards, olive-groves, and orchards, waste by war and pestilence, and crying out for human beings to come and till it once more.
There is no force left in Italy now, which can oppose him. Hardly any left in the Roman world. The plague is come; to add its horrors to all the other horrors of the time—the true old plague, as far as I can ascertain; bred, men say, from the Serbonian bog; the plague which visited Athens in the time of Socrates, and England in the seventeenth century: and after the plague a famine; woe on woe, through all the dark days of Justinian the demon-emperor. The Ostrogoths, as you know, were extinct as a nation. The two deluges of Franks and Allmen, which, under the two brothers Buccelin and Lothaire, all on foot (for the French, as now, were no horsemen), had rolled into Italy during the Gothic war, had been swallowed up, as all things were, in the fatal gulf of Italy. Lothaire and his army, returning laden with plunder, had rotted away like sheep by Lake Benacus (Garda now) of drink, and of the plague. Buccelin, entrenched among his plunder-waggons by the Volturno stream in the far south, had waited in vain for that dead brother and his dead host, till Narses came on him, with his army of trained Herules and Goths; the Francisc axe and barbed pike had proved useless before the arrows and the cavalry of the Romans; and no more than five Allmen, says one, remained of all that mighty host. Awful to think of: 75,000 men, they say, in one column, 100,000 in the other: and like water they flowed over the land; and like water they sank into the ground, and left no trace.
And now Narses, established as exarch of Ravenna, a sort of satrap, like those of the Persian Emperors, and representing the Emperor of Constantinople, was rewarded for all his conquests and labours by disgrace. Eunuch-like, he loved money, they said; and eunuch-like, he was harsh and cruel. The Empress Sophia, listening too readily to court-slanders, bade him ‘leave to men the use of arms, and come back to the palace, to spin among the maids.’—‘Tell her,’ said the terrible old imp, ‘I will spin her such a thread as she shall not unravel.’
He went, superseded by Longinus; but not to Constantinople. From Naples he sent (so says Paul the Deacon) to Alboin, and bade him come and try his fortune as king of Italy. He sent, too, (so says old Paul) presents to tempt the simple Lombard men—such presents as children would like—all fruits which grew in Italian orchards. Though the gold was gone, those were still left. Great babies they were, these Teutons, as I told you at the first; and Narses knew it well, and had used them for his ends for many a year.
Then were terrible signs seen in Italy by night; fiery armies fighting in the sky, and streams of blood aloft, foreshadowing the blood which should be shed.
Sent for or not, King Alboin came; and with him all his army, and a mighty multitude, women, and children, and slaves; Bavarians, Gepidæ, Bulgars, Sarmatæ, Pannonians, Sueves, and Noricans; whose names (says Paul) remain unto this day in the names of the villages where they settled. With Alboin, too, came Saxons, twenty thousand of them at the least, with wife and child. And Sigebert king of the Franks put Suevic settlers into the lands which the Saxons had left.
Alboin gave up his own Hungarian land to his friends the Avars, on the condition that he should have them back if he had to return. But return he never did, he nor his Lombard host. This is the end. The last invasion of Italy. The sowing, once for all, of an Italian people. Fresh nations were still pressing down to the rear of the Alps, waiting for their turn to enter the Fairy Land—not knowing, perhaps, that nothing was left therein, but ashes and blood:—but their chance was over now: a people were going into Italy who could hold what they got.
On Easter Tuesday, in the year of grace 568, they came, seemingly by the old road; the path of Alaric and Dietrich and the rest; the pass from Carniola, through which the rail runs now from Laybach to Trieste. It must have been white, in those days, with the bones of nigh 200 years. And they found bisons, aurochsen, in the mountains, Paul says, and is not surprised thereat, because there are plenty of them in Hungary near by. An old man told him he had seen a skin in which fifteen men might lie side by side. None, you must know, are left now, save a very few in the Lithuanian forests. Paul goes out of his way to note this fact, and so shall I.
Alboin left a strong guard in Friuli, and Paul’s ancestor among them, under Gisulf his nephew, and Marphrais or master of the horse, who now became duke of Friuli and warden of the marches, bound to prevent the Avars following them into their new abode. Then the human deluge spread itself slowly over the Lombard plains. None fought with them, and none gainsaid; for all the land was waste. The plague of three years before, and the famine which followed it had, says Paul, reduced the world into primæval silence. The villages had no inhabitants but dogs; the sheep were pasturing without a shepherd; the wild birds swarmed unhurt about the fields. The corn was springing self-sown under the April sun, the vines sprouting unpruned, the lucerne fields unmown, when the great Lombard people flowed into that waste land, and gave to it their own undying name.
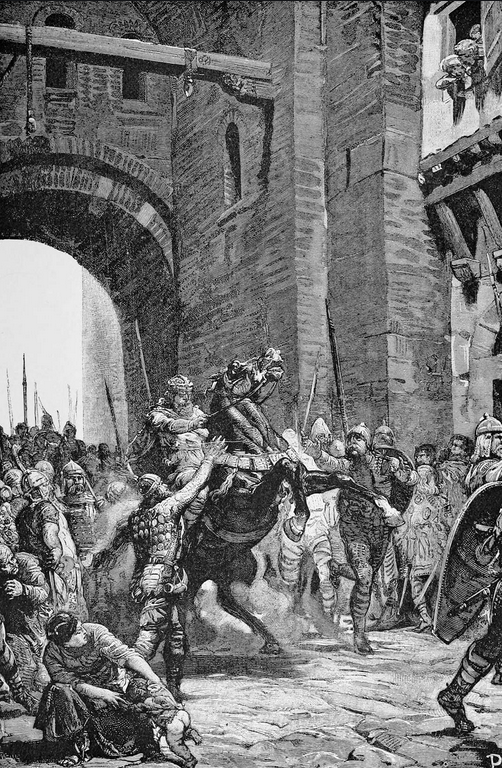

The scanty population, worn out with misery, fled to rocks and islands in the lakes, and to the seaport towns; but they seem to have found the Lombards merciful masters, and bowed their necks meekly to the inevitable yoke. The towns alone seem to have offered resistance. Pavia Alboin besieged three years, and could not take. He swore some wild oath of utter destruction to all within, and would have kept it. At last they capitulated. As Alboin rode in at St. John’s gate, his horse slipped up; and could not rise, though the grooms beat him with their lance-butts. A ghostly fear came on the Lombards. ‘Remember, lord king, thy cruel oath, and cancel it; for there are Christian folk in the city.’ Alboin cancelled his oath, and the horse rose at once. So Alboin spared the people of Pavia, and entered the palace of old Dietrich the Ostrogoth, as king of Italy, as far as the gates of Rome and Ravenna.
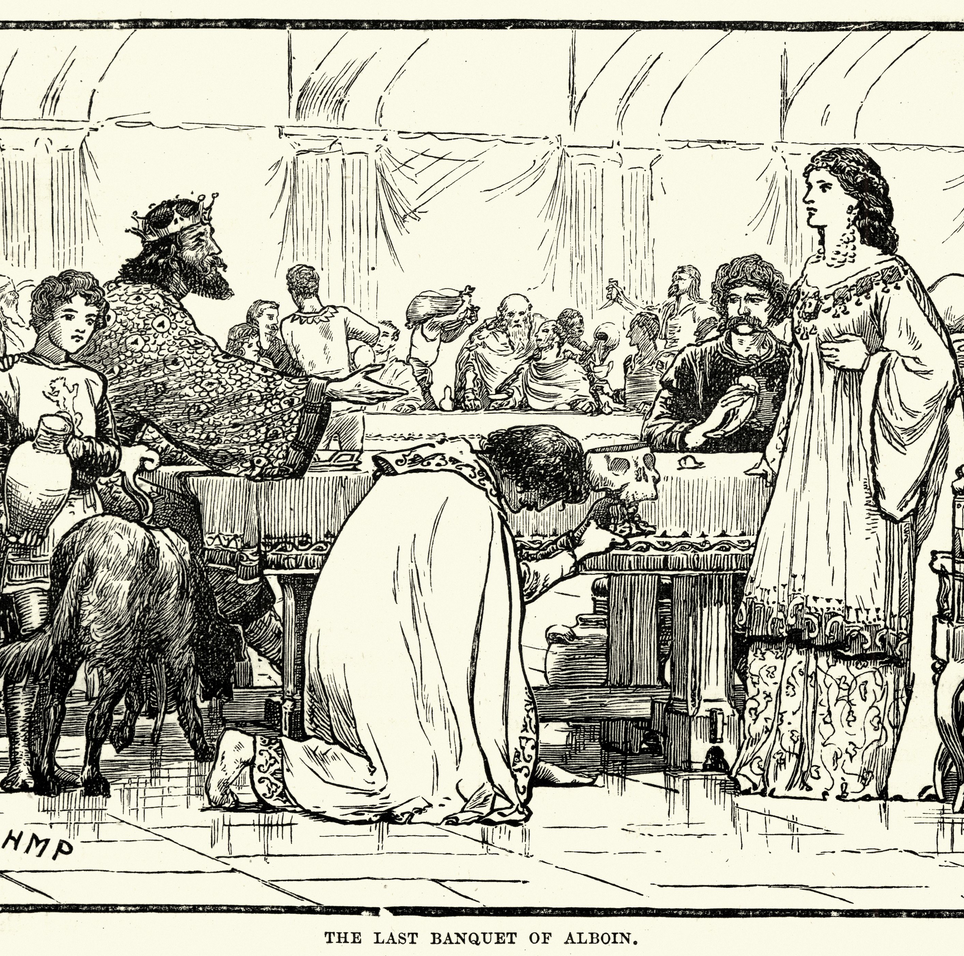

And what was his end? Such an end as he deserved; earned and worked out for himself. A great warrior, he had destroyed many nations, and won a fair land. A just and wise governor, he had settled North Italy on some rough feudal system, without bloodshed or cruelty. A passionate savage, he died as savages deserve to die. You recollect Rosamund his Gepid bride? In some mad drinking-bout (perhaps cherishing still his old hatred of her family) he sent her her father’s skull full of wine, and bade her drink before all. She drank, and had her revenge.
The story has become world-famous from its horror: but I suppose I must tell it you in its place.—How she went to Helmichis the shield-bearer, and he bade her get Peredeo the Kemper-man to do the deed: and how Peredeo intrigued with one of her bower-maidens, and how Rosamund did a deed of darkness, and deceived Peredeo; and then said to him, I am thy mistress; thou must slay thy master, or thy master thee. And how he, like Gyges in old Herodotus’s tale, preferred to survive; and how Rosamund bound the king’s sword to his bedstead as he slept his mid-day sleep, and Peredeo did the deed; and how Alboin leapt up, and fought with his footstool, but in vain. And how, after he was dead, Rosamund became Helmichis’ leman, as she had been Peredeo’s, and fled with him to Ravenna, with all the treasure and Alpswintha, Alboin’s daughter by the Frankish wife; and how Longinus the exarch persuaded her to poison Helmichis, and marry him; and how she gave Helmichis the poisoned cup as he came out of the bath, and he saw by the light of her wicked eyes that it was poison, and made her drink the rest; and so they both fell dead. And then how Peredeo and the treasure were sent to the Emperor at Constantinople; and how Peredeo slew a great lion in the theatre; and how Tiberius, when he saw that he was so mighty a man of his hands, bade put his eyes out; and how he hid two knives in his sleeves, and slew with them two great chamberlains of the Emperor; and so died, like Samson, says old Paul, having got good weregeld for the loss of his eyes—a man for either eye.
And old Narses died at Rome, at a great age; and they wrapt him in lead, and sent him to Byzant with all his wealth. But some say that while he was still alive, he hid his wealth in a great cistern, and slew all who knew of it save one old man, and swore him never to reveal the place. But after Narses’ death that old man went to Constantinople to Tiberius the Cæsar, and told him how he could not die with that secret on his mind; and so Tiberius got all the money, so much that it took many days to carry away, and gave it all to the poor, as was his wont. A myth—a fable: but significant, as one more attempt to answer the question of all questions in a Teuton’s mind—What had become of the Nibelungen hoard? What had become of all the wealth of Rome?









