Editor’s Note: The following account is taken from Historical Tales, by Charles Morris (published 1896).
Prasutagus, the king of the Icenians, a tribe of the ancient Britons, had amassed much wealth in the course of a long reign. On his death, in order to secure the favor of the Romans, now masters of the island, he left half his wealth by will to the emperor and half to his two daughters. This well-judged action of the barbarian king did not have the intended effect. No sooner was he dead than the Romans in the vicinity claimed the whole estate as theirs, ruthlessly pillaged his house, and seized all his effects.
This base brigandage roused Boadicea, the widowed queen, to a vigorous protest, but with the sole result of bringing a worse calamity upon her head. She was seized and cruelly scourged by the ruthless Romans, her two daughters were vilely maltreated, and the noblest of the Icenians were robbed of their possessions by the plunderers, who went so far as to reduce the slavery the near relatives of the deceased king.

Roused to madness by this inhuman treatment, the Icenians broke into open revolt. They were joined by a neighboring state, while the surrounding Britons, not yet inured to bondage, secretly resolved to join the cause of liberty. There had lately been planted a colony of Roman veterans at Camalodunum (Colchester), who had treated the Britons cruelly, driven them from their houses, and insulted them with the names of slaves and captives; while the common soldiers, a licentious and greedy crew, still further degraded and robbed the owners of the land.
The invaders went too far for British endurance, and brought a terrible retribution upon themselves. Paulinus Suetonius, an able officer, when then commanded in Britain, was absent on an expedition to conquer the island of Mona. Of this expedition the historian Tacitus gives a vivid account. As the boats of the Romans approached the island they beheld on the shore the Britons prepared to receive them, while through their ranks rushed their women in funeral attire, their hair flying loose in the wind, flaming torches in their hands, and their whole appearance recalling the frantic rage of the fabled Furies. Nearby, ranged in order, stood the venerable Druids, or Celtic priests, with uplifted hands, at once invoking the gods and pouring forth imprecations upon the foe.
The novelty and impressiveness of this spectacle filled the Romans with awe and wonder. They stood in stupid amazement, riveted to the spot, and a mark for the foe had they been attacked. From this brief paralysis the voice of their general recalled them, and, ashamed of being held in awe by a troop of women and a band of fanatic priests, they rushed to the assault, cut down all before them, and set fire to the edifices and the sacred groves of the island with the torches which the Britons themselves had kindled.

But Suetonius had chosen a perilous time for this enterprise. During his absence the wrongs of the Icenians and the exhortations of Boadicea had roused a formidable revolt, and the undefended colonies of the Romans were in danger.
In addition to the actual peril the Romans were frightened with dire omens. The statue of victory at Camalodunum fell without any visible cause, and lay prostrate on the ground. Clamors in a foreign accent were heard in the Roman council chamber, the theatres were filled with the sound of savage howlings, the sea ran purple as with blood, the figures of human bodies were traced on the sands, and the image of a colony in ruins was reflected from the waters of the Thames.
These omens threw the Romans into despair and filled the minds of the Britons with joy. No effort was made by the soldiers for defense, no ditch was dug, no palisade erected, and the assault of the Britons found the colonists utterly unprepared. Taken by surprise, the Romans were overpowered, and the colony was laid waste with fire and sword. The fortified temple alone held out, but after a two days’ siege it also was taken, and the legion which marched to its relief was cut to pieces.


Boadicea was now the leading spirit among the Britons. Her wrongs had stirred them to revolt, and her warlike energy led them to victory and revenge. But she was soon to have a master-spirit to meet. Suetonius, recalled from the island of Mona by tidings of rebellion and disaster, marched hastily as far as London, which was even then the chief residence of the merchants and the centre of trade and commerce of the island.
His army was small, not more than ten thousand men in all. That of the Britons was large. The interests of the empire were greater than those of any city, and Suetonius found himself obliged to abandon London to the barbarians, despite the supplications of its imperilled citizens. All he would agree to was to take under his protection those who chose to follow his banner. Many followed him, but many remained, and no sooner had he marched out than the Britons fell in rage on the settlement, and killed all they found. In like manner they ravaged Verulamium (St. Albans). Seventy thousand Romans are said to have been put to the sword.

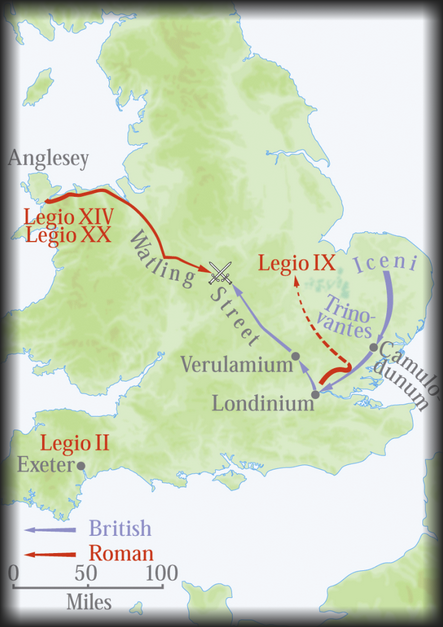
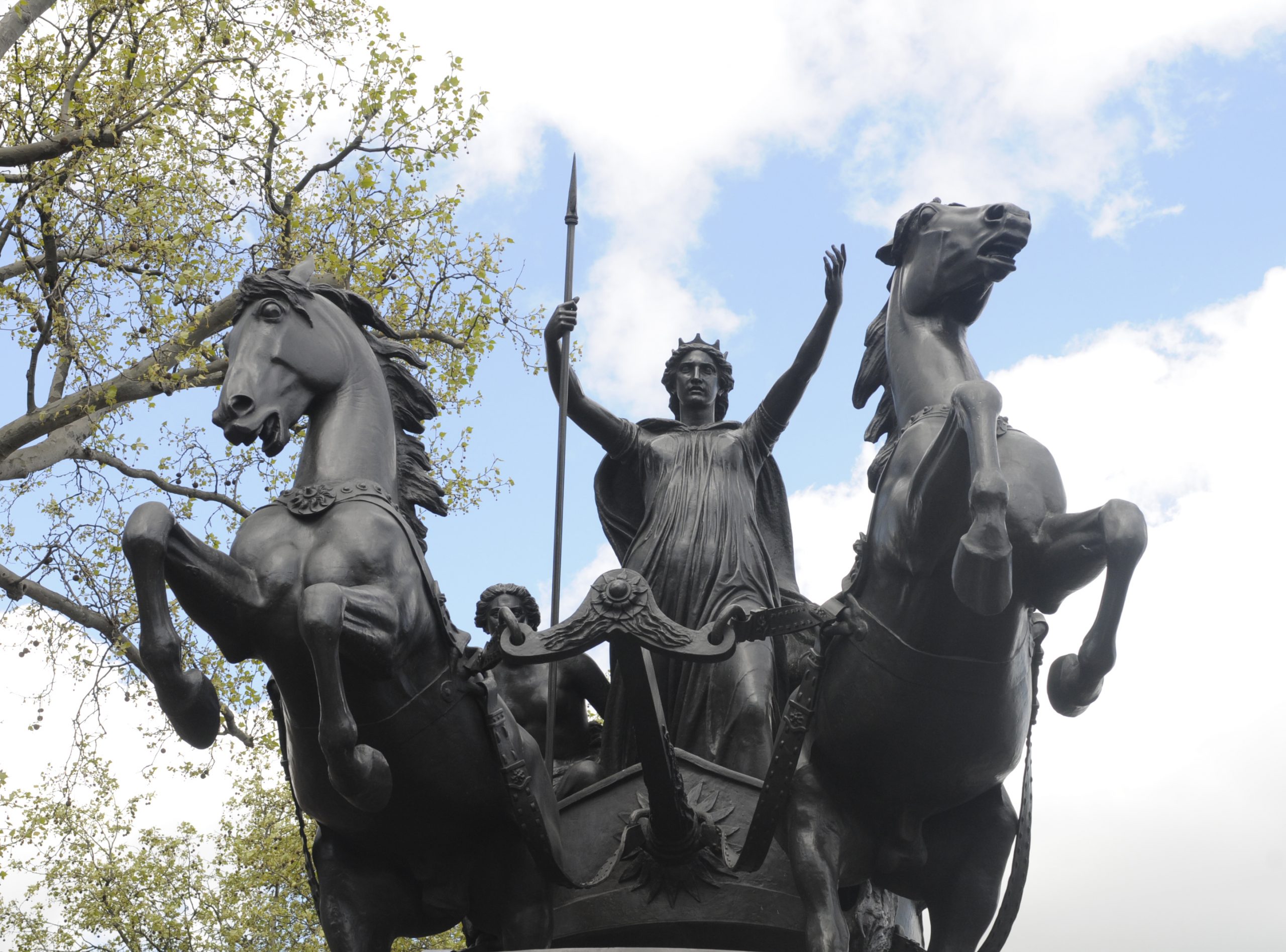
Meanwhile Suetonius marched through the land, and at length the two armies met. The skilled Roman general drew up his force in a place where a thick forest sheltered the rear and flanks, leaving only a narrow front open to attack. Here the Britons, twenty times his number, and confident of victory, approached. The warlike Boadicea, tall, stern of countenance, her hair hanging to her waist, a spear in her hand, drove along their front in a warlike car, with her two daughters by her side, and eloquently sought to rouse her countrymen to thirst for revenge.
Telling them of the base cruelty with which she and her daughters had been treated, and painting in vivid words the arrogance and insults of the Romans, she besought them to fight for their country and their homes. “On this spot we must either conquer or die with glory,” she said. “There is no alternative. Though I am a woman, my resolution is fixed. The men, if they prefer, may survive with infamy and live in bondage. For me there is only victory or death.”
Stirred to fury by her words, the British host poured like a deluge on their foes. But the Roman arms and discipline proved far too much for barbarian courage and ferocity. The British were repulsed, and, rushing forward in a wedge shape, the legions cut their way with frightful carnage through the disordered ranks. The cavalry seconded their efforts. Thousands fell. The rest took to flight. But the wagons of the British, which had been massed in the rear, impeded their flight, and a dreadful slaughter, in which neither sex nor age was spared, ensued. Tacitus tells us that eighty thousand Britons fell, while the Roman slain numbered no more than four hundred men.
Boadicea, who had done her utmost to rally her flying hosts, kept to her resolution. When all was lost, she took poison, and perished upon the field where she had vowed to seek victory or death. With her decease the success of the Britons vanished. Though they still kept the field, they gradually yielded to the Roman arms, and Britain became in time a quiet and peaceful part of the great empire of Rome.











4.5