Editor’s note: The following is extracted from Famous Privateersmen and Adventurers of the Sea, by Charles H.L. Johnston (published 1911).

The torches fluttered from the walls of a burial vault in ancient Venice. Two shrouded figures leaned over the body of a dead warrior, and, as they gazed upon the wax-like features, their eyes were filled with tears.
“See,” said the taller fellow. “He has indeed led the stalwart life. Here are five and thirty wounds upon the body of our most renowned compatriot. He was a true hero.”
“You speak correctly, O Knight,” answered the other. “Carlo Zeno was the real warrior without fear and without reproach. He has fared badly at the hands of the Republic. But then, is this not life? Those most worthy seem never to receive their just compensation during their living hours. It is only when they are dead that a tardy public gives them some recognition of the great deeds which they have done, the battles which they have fought, and the honor which they have brought to their native land. Alas! poor Zeno! He, the true patriot, has had but scant and petty praise.”

So saying the two noble Venetians covered the prostrate form of the dead warrior—for they had lifted the brown robe which enshrouded him—and, with slow faltering steps, they left the gloomy chamber of death.
Who was this Venetian soldier, who, covered with the marks of battle, lay in his last sleep? Who, this hero of war’s alarms? This patriotic leader of the rough-and-ready rovers of the sea?
It was Carlo Zeno, a man of the best blood of Venice, who, commanding fighting men and fighting ships, had battled strenuously and well for his native country.
The son of Pietro Zeno and Agnese Dandolo, this famous Venetian had been well bred to the shock of battle, for his father was for some time Governor of Padua, and had won a great struggle against the Turks, when the careening galleys of the Venetian Squadron grappled blindly with the aggressive men of the Ottoman Empire. There were ten children in the family and little Carlo was named after the Emperor Charles IV, who sent a retainer to the baptism of the future seaman, saying, “I wish the child well. He has a brave and noble father and I trust that his future will be auspicious.”

Little Carlo was destined for the Church, and, with a Latin eulogium in his pocket (which his Venetian school-master had written out for him) was sent to the court of the Pope at Avignon. The sweet-faced boy was but seven years of age. He knelt before the prelate and his retainers, reciting the piece of prose with such precision, grace, and charm, that all were moved by his beauty, his memory, his spirit, and his liveliness of person.
“You are indeed a noble youth,” cried the Pope. “You shall come into my household. There you shall receive an education and shall be a canon of the cathedral of Patras, with a rich benefice.”
But little Carlo did not remain. Although dressed like a mimic priest and taught with great care, the hot blood of youth welled in his veins and made him long for a life more active and more dangerous. So he looked about for adventure so thoroughly that he was soon able to have his first narrow escape, and a part in one of those many brawls which were to come to him during his career of war and adventure.
Sent by his relations to the University of Padua, he was returning to Venice from the country, one day, when a man leaped upon him as he walked down a narrow road.
“Who are you?” cried Carlo fearfully.
But the fellow did not answer. Instead, he struck him suddenly with a stout cudgel, knocked him senseless on the turf, took all the valuables which he had, and ran silently away into the gloom.
Little Carlo came to his senses after many hours, and, staggering forward with weakened steps, reached Mestre, where kind friends dressed his wounds.
“I shall catch this assailant,” cried he, when he had revived. “He shall rue the day that he ever touched the person of Carlo Zeno.” And forthwith he secured a number of bloodhounds with which to track the cowardly ruffian of the highway.
Luck was with the future commander of the galleons and fighting men. He ran the scurvy assailant to earth, like a fox. He captured him, bound him and handed him over to the justice of Padua, where, for the heinousness of the offense, the man was executed. So ended the first conflict in which the renowned Carlo Zeno was engaged, successfully as did most of his later battles.
Not long afterwards young Zeno returned to his studies at the University, but here, as a lover of excitement, he fell into bad company. Alas! He took to gambling, and frittered away all of his ready money, so that he had to sell his books in order to play. The profit from these was soon gone. He was bankrupt at the early age of seventeen.
Ashamed to go home, the future sea rover disappeared from Padua and joined a fighting band of mercenaries (paid soldiers) who were in the employ of a wealthy Italian Prince. He was not heard of for full five years. Thus, his relatives gave him up for dead, and, when, one day, he suddenly stalked into the house of his parents, his brothers and sisters set up a great shout of wonder and amazement. “Hurrah!” cried they, “the dead has returned to his own. This is no ghost, for he speaks our own native tongue. Carlo Zeno, you shall be given the best that we have, for we believed that you had gone to another world.”
Pleased and overwhelmed with affection, young Carlo stayed for a time with his family, and then—thinking that, as he had been trained for the priesthood, he had best take charge of his canonry of Patras—he went to Greece.
“Hah! my fine fellow,” said the Governor, when he first saw him, “I hear that you are fond of fighting. It is well. The Turks are very troublesome, just now, and they need some stout Venetian blood to hold them in check. You must assist us.”
“I’ll do my best,” cried Zeno with spirit, and, he had not been there a week before the Ottomans swooped down upon the city, bent upon its demolition. The young Venetian sallied forth, with numerous fighting men, to meet them, and, in the first clash of arms, received such a gaping wound that he was given up for dead. In fact, when carried to the city, he was considered to be without life, was stretched upon a long settee, was clothed in a white sheet, and prepared for interment. But in the early morning he suddenly opened his eyes, gazed wonderingly at the white shroud which covered him, and cried, with no ill humor,
“Not yet, my friends. Carlo Zeno will disappoint all your fondest hopes. Once more I am of the world.”
And, so saying, he scrambled to his feet, much to the dismay of the sorrowing Venetians, who had been carefully spreading a number of flowers upon the prostrate form of the supposedly dead warrior.
But so weak was the youthful hero that he had to be taken to Venice in order to recover. When strong again he resumed his studies for the ministry and was sent to Patras, a city that was soon threatened by an army of twelve thousand Cypriots and Frenchmen.
“Here, Zeno,” cried the Bishop of Patras to the virile young stripling. “We have seven hundred riders in our city. With this mere handful, you must defend us against our enemies. The odds are fifteen to one against you. But you must struggle valiantly to save our beautiful capital.”
“Aye! Sire!” cried the youthful student of church history. “I shall do my best to free your capital from these invaders. May the God of Hosts be with us! My men salute you.”
So saying the valiant youth led his small and ill drilled company against the besiegers, and, so greatly did he harass his adversaries, that they abandoned the enterprise, at the end of six months; made peace; and retired.
“Hail to Zeno!” cried many of the soldiers. “He is a leader well worth our respect. Without him the great city would have surely fallen. Yea! Hail to young Zeno.”
These words of praise reached the ears of a certain Greek knight named Simon, and so roused his envy, that he audaciously accused Carlo of treachery, which was soon told to the hot-headed young warrior. He acted as one would well expect of him.
“I challenge you to single combat,” cried he. “The duel shall be fought in Naples under the eye of Queen Johanna.”
In vain Carlo’s friends besought him to forgive the loose-tongued Simon, his patron, the Bishop, exhausted his eloquence in the endeavor to reconcile the two. The hot blood of youth would out. It was fight and no compromise. But before the trial, the bold and unyielding soldier threw up his position with the Church and married a rich and noble lady of Clarenta, whose fortune well supplanted the large income which he had forfeited by his resignation.
Now honor called for deeds. Almost immediately he was obliged to leave for Naples in order to meet the detractor of his valor, and, to his surprise, the Queen spoke lightly of the quarrel. “It is a question of law,” said she. “An inquiry shall be had. There must be no bloodshed.”
An inquiry was therefore in order, and it was a thorough one. “Simon is in the wrong,” said the fellow acting as clerk for those sitting upon the case. “He must pay all the expenses to which Zeno has been put, and there shall be no duel.”
“My honor has been cleared,” cried Zeno. “I must return to Greece.” There, strange as it might seem, he was at once named Governor of a province, though not yet twenty-three. Events were going well with him. But his wife died, he was cheated of his dowry by her relations, and so he turned once more to Venice, saddened, older and nearly penniless. The wheel of fortune had turned badly for this leader of fighting men and future general of white-winged galleons of the sea.
But now there was a really good fight, such a fight as all true sailors love, a fight which tested the grit and courage of Zeno to the full. It was the first of those heroic deeds of arms which shed undying luster on his name, and marked him as a seaman of the first rank, a captain of true courage, resources and ambition.
The Genoese (or inhabitants of Genoa) and the Venetians, were continually at war in these days, and when, in patriotic zeal, Carlo Zeno seized the island of Tenedos, the Venetian Senate, fearing lest the Genoese would seek to recover the lost possession, sent a fleet of fifteen ships to guard it, under one Pietro Mocenigo. There were also two other vessels, one commanded by Carlo Zeno himself. The mass of galleys floated on to Constantinople, for the Greeks had allied themselves with the Genoese, had seized a Venetian man-of-war, which had been captured, and had then retired. Three lumbering hulks were left to protect the fair isle of Tenedos, under Zeno, the warlike Venetian.
“Aha,” said a Genoese seaman. “There are but three galleys left to save our isle of Tenedos. We shall soon take it with our superior force. Forward, O sailors! We’ll have revenge for the attack of the wild men from Venice.”
“On! on!” cried the Genoese seamen, and without further ado, twenty-two galleys careened forward, their white sails bellying in the wind, their hawsers groaning, spars creaking, and sailors chattering like magpies on a May morning.
Carlo Zeno had only three hundred regular soldiers and a few archers, but he occupied the suburbs of the town and waited for the attackers to land. This they did in goodly numbers, for the sea was calm and motionless, although it was the month of November.
“Men!” cried the intrepid Zeno, “you are few. The enemy are as numerous as blades of grass. Do your duty! Fight like Trojans, and, if you win, your grateful countrymen will treat you as heroes should be respected. Never say die, and let every arrow find an opening in the armor of the enemy.”
The Genoese came on with shouts of expectancy, but they were met with a far warmer reception than they had anticipated. The air was filled with flying arrows, as, crouching low behind quickly constructed redoubts, the followers of the stout-souled Zeno busily stretched their bowstrings, and shot their feathered barbs into the mass of crowding seamen. Savage shouts and hoarse cries of anguish, rose from both attackers and attacked, while the voice of Zeno, shrilled high above the battle’s din, crying: “Shoot carefully, my men, do not let them defeat us, for the eyes of Venice are upon you.” So they struggled and bled, until the shadows began to fall, when, realizing that they were unable to take the courageous Venetians, the Genoese withdrew to their ships.
There was laughter and song around the camp fires of Zeno’s little band, that night, but their leader spoke critically of the morrow.
“Sleep well, my men,” said he, “for I know that our foes are well angered at the beating we have given them. Next morn we shall again be at war. Let us keep our courage and have as a battle cry, ‘Venice! No retreat and no quarter!’”
When morning dawned the Genoese were seen to land engines of war, with the apparent intention of laying siege to the town. Their preparations showed that they meant to attack upon the side farthest from the castle, so Carlo Zeno, the quick-witted, placed a number of his men in ambush, among a collection of half-ruined and empty houses which stood in that quarter. “Stay here, my men,” said he, “and when the enemy has advanced, charge them with fury. We must win today, or we will be disgraced.”
Meanwhile the rest of the Venetians had retreated inland, and, crouching low behind a screen of brush, waited patiently for the Genoese to come up. “Be cautious,” cried Zeno, “and when the enemy is within striking distance, charge with all the fury which you possess.”
“Aye! Aye! Good master,” cried the stubborn soldiers. “We mark well what you tell us.”
Not long afterwards the attacking party came in view, and, without suspecting what lay in front, advanced with quick gait towards the supposedly defenseless town. But suddenly, with a wild yell, the followers of Zeno leaped from behind the screening bushes, and dashed towards them. At the same instant, the soldiers who had been placed in hiding, attacked suddenly from the rear. Arrows poured into the ranks of the Genoese, and they fell like wheat before the scythe of the reaper. Hoarse shouts, groans, and cries of victory and death, welled above the battle’s din.
In the midst of this affair Carlo Zeno gave a cry of pain. An arrow (poisoned ’tis said) had entered his leg and struck him to the ground. But, nothing daunted, he rose to cry shrilly to his men, “On! On! Drive them to the ocean.” And, so well did his soldiers follow these commands, that the Genoese fled in confusion and disorder to their ships. The day was won.
As was natural, Zeno paid no attention to his wound, and, when the enemy hurried to shore the next day for another attack, they were greeted with such a terrific discharge of artillery that they gave up their idea of capturing the island and sailed away amidst cries of derision from the delighted Venetians.

“Hurrah!” cried they. “Hurrah for Zeno!” But so exhausted was the intrepid leader by reason of his wound that he fell into a spasm as if about to die. His iron constitution pulled him through, however, and soon he and the faithful band returned to Venice, covered with glory, and full satisfied with their hard won victory.
The daring Zeno was well deserving of praise, for he had beaten a fleet and an army by sheer genius, with three ships and a handful of men. To Venice had been preserved the valuable island which guards the entrance to the Dardanelles, and to her it was to remain for years, although the Genoese tried many times and oft to wrest it from her grasp.
Now came another struggle, the war of Chioggia, a struggle in which Carlo Zeno played a great and noble part, a part, in fact, that has made his name a byword among the grateful Venetians: a part in which he displayed a leadership quite equal to that of a Drake, or a Hawkins, and led his fighting galleons with all the courage of a lion. Hark, then, to the story of this unfortunate affair! Hark! and let your sympathy be stirred for Carlo Zeno, the indefatigable navigator of the clumsy shipping of the Italian peninsula!
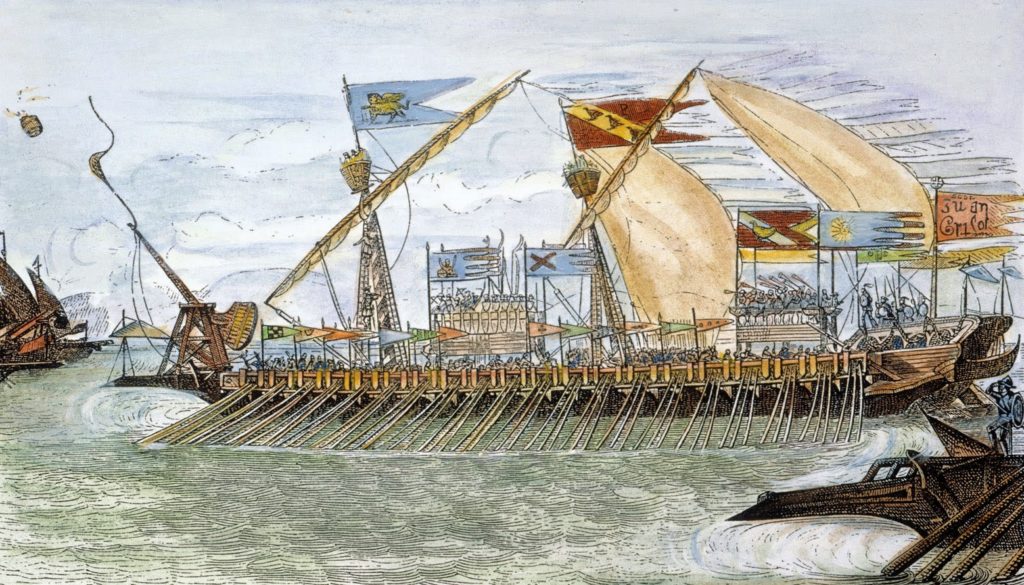

For years the Republics of Genoa and Venice remained at peace, but, for years the merchants of the two countries had endeavored to outwit each other in trade; and, thus, when the Genoese seized several Venetian ships with rich cargoes, in 1350, and refused to give them up, war broke out between the rival Republics. In two engagements at sea, the Venetians were defeated; but in a third they were victorious, and forever sullied the banner of St. Mark, which flew from their Admiral’s mast-head, by causing nearly five thousand prisoners of war to be drowned. Fired by a desire for immediate revenge upon their foe, the Genoese hurried a mighty fleet to sea, and ravaged the Italian coast up to the very doors of Venice itself. Several other engagements followed, in most of which the Venetians were defeated; and then there were twenty years of peace before another conflict.
Finally war broke out afresh. Angry and vindictive, the Genoese bore down upon the Venetian coast in numerous lumbering galleys, determined—this time—to reach Venice itself, and to sack this rich and populous city. With little difficulty they captured Chioggia, a seaport, a populous city and the key to the lagoons which led to the heart of the capital. They advanced to the very outskirts of Venice, and their cries of joyous vindictiveness sounded strangely near to the now terrified inhabitants, who, rallying around their old generals and city fathers, were determined to fight to the last ditch.
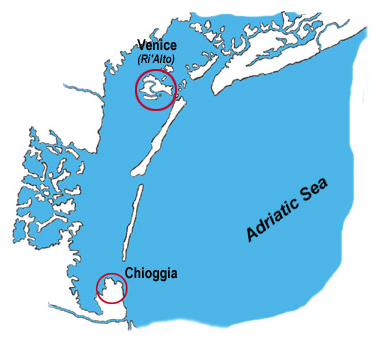

As winter came, the victoriously aggressive Genoese retreated to Chioggia, withdrawing their fleet into the safe harbor to await the spring; leaving only two or three galleys to cruise before the entrance, in case the now angered Venetians should attack. But they were to be rudely awakened from their fancied seclusion.
“Lead us on, O Pisani,” the Venetians had cried in the broad market space of their beloved city. “We must and will drive these invaders into their own country. Never have we received before such insults. On! On! to Chioggia.”

So, silent and vengeful, the Venetian fleet stole out to sea on the evening of December twenty-first. There were thirty-four galleys, sixty smaller armed vessels, and hundreds of flat-bottomed boats. Pisani was in the rear, towing two heavy, old hulks, laden with stones, to sink in the entrance of the harbor and bottle up the fleet, even as the Americans were to sink the Merrimac in the Harbor of Santiago, many years afterwards.
The Genoese were unready. The cruisers, on duty as sentinels, were not where they should have been, and so the gallant Pisani scuttled the hulks across the harbor entrance and caught the bold marauders like rats in a trap. The fleet of the enemy was paralyzed, particularly as another river’s mouth, some two miles southward, was also blockaded. Smiles of satisfaction shone upon the faces of the outraged Venetians.
Carlo Zeno was hurrying up with a strong fleet manned by veteran seamen, but the now victorious followers of Pisani wished to return to Venice.
“It is the Christmas season,” cried many. “We have fought like lions. We have shut up our enemy. We have averted the extreme danger. Let us return to our wives and our children!”
“You cannot go,” said Pisani, sternly. “You are the entire male population of Venice. Without you the great expedition will come to naught, and all of our toil will have been thrown away. Only be calm. Carlo Zeno will soon be here, and we can then take Chioggia!”
Alas! Like Columbus, he saw himself upon the verge of losing the result of all his labor for lack of confidence in him upon the part of his men. He could not keep them by force, so wearily and anxiously he scanned the horizon for signs of an approaching sail.

The days went slowly by for the lion-hearted Pisani. Carlo Zeno did not come. Day after day the valiant leader fearfully looked for the white-winged canvas of a Venetian galleon, but none came to view. On the thirtieth day of December his men were very mutinous.
“We will seize the ships and return tomorrow to Venice,” cried several. “We have had enough of war. Our wives and daughters cry to us to return.”
Pisani was desperate.
“If Carlo Zeno does not come in forty-eight hours, the fleet may return to Lido,” said he. “Meanwhile, keep your guns shooting at the enemy. We must make these Genoese feel that we shall soon attack in force.”
But Pisani’s heart was leaden. Where, yes, where was Zeno? New Year’s Day came, and, by his promise, he must let the Venetians go. What did this mean for him? It meant the fall of Venice, the end of the Republic, the destruction of the population with all that they possessed. He, their idol, their leader for ten days, could no longer lead, for the Venetians could not bear a little cold and hardship for his sake. Sad, yes, sad, indeed, was the face of the stout seaman as he gave one last despairing glance at the horizon.
Ha! What was that? A thin, white mark against the distant blue! It grew larger and clearer. It was the sail of a galley. Another, and another, and another hove in sight,—eighteen in all, and driving along swiftly before a heavy wind. But, were they hostile, or friendly? That was the question. Was it Zeno, or were these more galleons of the Genoese? Then, joy shone in the keen eyes of Pisani, for the banner of St. Mark fluttered from the peak of the foremost ship, and floated fair upon the morning breeze. Hurrah! It was Carlo Zeno, the lion-hearted.
God speed brave Zeno! He had been twice wounded in fights along the coast, en route, but nothing could diminish his energy, or dampen his ardor. He had laid waste the Genoese coast; he had intercepted convoys of grain; he had harassed the enemy’s commerce in the East, and he had captured a huge vessel of theirs with five hundred thousand pieces of gold. Marvellous Zeno! Brave, courageous Venetian sea-dog, you are just in the nick of time!
“Thanks be to Heaven that you have come,” cried Pisani, tears welling to his eyes. “Now we will go in and take Chioggia. It means the end of the war for us. Again, I say, thanks be to Heaven.”

With renewed hope and confidence the Venetians now pushed the siege. Seeing that their fleet could never escape, the Genoese started to dig a canal to the open sea, by which the boats could be brought off during the night. The work was begun, but Carlo Zeno discovered it in time. Volunteers were called for, a force was soon landed, and, under the leadership of Zeno, marched to intercept the diggers of this, the only means of escape.
“The Venetians are going towards ‘Little Chioggia,’” cried many of the Genoese. “We must hasten there to stop them.”
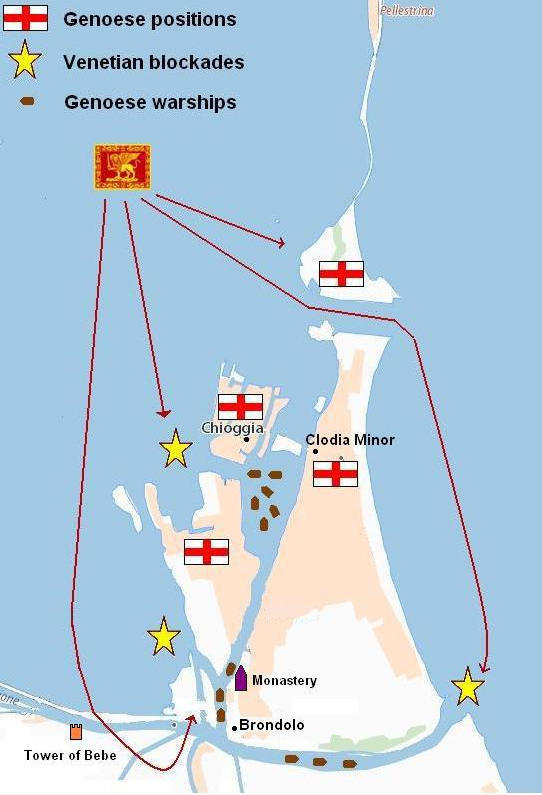
But Zeno had only made a feint in this direction. Throwing his main force in the rear of the Genoese, he soon began to cut them up badly. They were seized with a panic. They fled towards the bridge of Chioggia, trampling upon each other as they ran, pursued and slashed to ribbons by Zeno’s men. The bridge broke beneath the weight of the fugitives and hundreds were drowned in the canal, while thousands perished near the head of this fateful causeway. It was a great and signal victory for Zeno; the intrepid sea-dog and campaigner on land.
This was a death blow. That night some of the garrison hastened to desert, and, as the siege progressed, the drinking water began to fail, the food gave out, and starvation stared the holders of Chioggia in the face. On the twenty-fourth of June the city surrendered; and four thousand one hundred and seventy Genoese, with two hundred Paduans, ghastly and emaciated, more like moving corpses than living beings, marched out to lay down their arms. Seventeen galleys, also, were handed over to the Venetians: the war-worn relics of the once powerful fleet which had menaced Venice itself.

As a feat of generalship, Pisani’s blockade of the Genoese fleet is rivalled by Sampson’s blockade of Cervera’s squadron at Santiago in 1898, and the military operation by which Carlo Zeno tempted the garrison of Brondolo into the trap which he had set for them, and drove them, like a flock of sheep into Chioggia, by sunset, is surely a splendid feat of arms. All honor to this intrepid sea-dog of old Venice!
How fickle is Dame Fortune! Jealous of the reputation of this noble Venetian, the patricians, whose advice, during the war, he had consistently declined to follow; refused to make him a Doge of the City. It was thought that the election of the bravest captain of the day might be dangerous to the Republic. Instead of doing him honor, they imprisoned him; and was he not the noblest patriot of them all?
When over seventy years of age, the greatest and truest Venetian, loaned a small sum of money to the Prince Carrara, once a power in Venetian politics. He had saved his country from destruction. He had served her with the most perfect integrity. Yet, he reaped the reward which fell to the share of nearly every distinguished Venetian; he was feared by the government; hated by the nobles whom he had outstripped in honor, and was condemned to prison by men who were not worthy to loose the latchet of his shoes. Although he had often paid the mercenary soldiers to fight for Venice, in the War of Chioggia, from his own pocket, he was sent to jail for loaning money to an unfortunate political refugee.

When called before the Council of Ten on the night of the twentieth of January, 1406, the warrant for his examination authorized the use of torture. But even the Ten hesitated at this.
“He is a brave man,” said one. “Pray allow him to go untouched.”
The prisoner admitted that he had loaned the money. His explanation was both honorable and clear. But the Ten were obdurate that night.
“He shall go to the Pozzi prison for a year,” said they. “Besides this, he shall suffer the perpetual loss of all offices which he has held.”
Like a brave man, Carlo Zeno accepted the sentence without a murmur, and his sturdy frame did not suffer from the confinement. For twelve years longer he lived in perfect health; made a pilgrimage to Jerusalem; commanded the troops of the Republic once again; defeated the Cypriots, and died peacefully, a warrior with a name of undiminished luster, most foully tarnished by his own compatriots. His is a reputation of undying glory, that of his judges is that of eternal shame. All honor to Carlo Zeno, the valorous Venetian, who could fight a ship as well as a squadron of foot soldiers on land! Salve, Venetia!











I love these. They’re what makes MOTW something beyond a blog. It’s a resource.
5