Editor’s note: The following is extracted from Myths and Legends of the Celtic Race, by T. W. Rolleston (published 1911). All spelling in the original.
Earliest References
In the chronicles of the classical nations for about five hundred years previous to the Christian era there are frequent references to a people associated with these nations, sometimes in peace, sometimes in war, and evidently occupying a position of great strength and influence in the Terra Incognita of Mid-Europe. This people is called by the Greeks the Hyperboreans or Celts, the latter term being first found in the geographer Hecatæsus, about 500 B.C.
Herodotus, about half a century later, speaks of the Celts as dwelling “beyond the pillars of Hercules”—i.e., in Spain—and also of the Danube as rising in their country.
Aristotle knew that they dwelt “beyond Spain,” that they had captured Rome, and that they set great store by warlike power. References other than geographical are occasionally met with even in early writers. Hellanicus of Lesbos, an historian of the fifth century B.C., describes the Celts as practising justice and righteousness. Ephorus, about 350 B.C., has three lines of verse about the Celts in which they are described as using “the same customs as the Greeks”—whatever that may mean—and being on the friendliest terms with that people, who established guest friendships among them. Plato, however, in the “Laws,” classes the Celts among the races who are drunken and combative, and much barbarity is attributed to them on the occasion of their irruption into Greece and the sacking of Delphi in the year 273 B.C. Their attack on Rome and the sacking of that city by them about a century earlier is one of the landmarks of ancient history.
The history of this people during the time when they were the dominant power in Mid-Europe has to be divined or reconstructed from scattered references, and from accounts of episodes in their dealings with Greece and Rome, very much as the figure of a primæval monster is reconstructed by the zoologist from a few fossilised bones. No chronicles of their own have come down to us, no architectural remains have survived; a few coins, and a few ornaments and weapons in bronze decorated with enamel or with subtle and beautiful designs in chased or repoussé work—these, and the names which often cling in strangely altered forms to the places where they dwelt, from the Euxine to the British Islands, are well-nigh all the visible traces which this once mighty power has left us of its civilisation and dominion. Yet from these, and from the accounts of classical writers, much can be deduced with certainty, and much more can be conjectured with a very fair measure of probability. The great Celtic scholar whose loss we have recently had to deplore, M. d’Arbois de Jubainville, has, on the available data, drawn a convincing outline of Celtic history for the period prior to their emergence into full historical light with the conquests of Cæsar, and it is this outline of which the main features are reproduced here.
The True Celtic Race
To begin with, we must dismiss the idea that Celtica was ever inhabited by a single pure and homogeneous race. The true Celts, if we accept on this point the carefully studied and elaborately argued conclusion of Dr. T. Rice Holmes, supported by the unanimous voice of antiquity, were a tall, fair race, warlike and masterful, whose place of origin (as far as we can trace them) was somewhere about the sources of the Danube, and who spread their dominion both by conquest and by peaceful infiltration over Mid-Europe, Gaul, Spain, and the British Islands. They did not exterminate the original prehistoric inhabitants of these regions—palæolithic and neolithic races, dolmen-builders and workers in bronze—but they imposed on them their language, their arts, and their traditions, taking, no doubt, a good deal from them in return, especially, as we shall see, in the important matter of religion. Among these races the true Celts formed an aristocratic and ruling caste. In that capacity they stood, alike in Gaul, in Spain, in Britain, and in Ireland, in the forefront or armed opposition to foreign invasion. They bore the worst brunt of war, of confiscations, and of banishment. They never lacked valour, but they were not strong enough or united enough to prevail, and they perished in far greater proportion than the earlier populations whom they had themselves subjugated. But they disappeared also by mingling their blood with these inhabitants, whom they impregnated with many of their own noble and virile qualities. Hence it comes that the characteristics of the peoples called Celtic in the present day, and who carry on the Celtic tradition and language, are in some respects so different from those of the Celts of classical history and the Celts who produced the literature and art of ancient Ireland, and in others so strikingly similar. To take a physical characteristic alone, the more Celtic districts of the British Islands are at present marked by darkness of complexion, hair, &c. They are not very dark, but they are darker than the rest of the kingdom. But the true Celts were certainly fair. Even the Irish Celts of the twelfth century are described by Giraldus Cambrensis as a fair race.
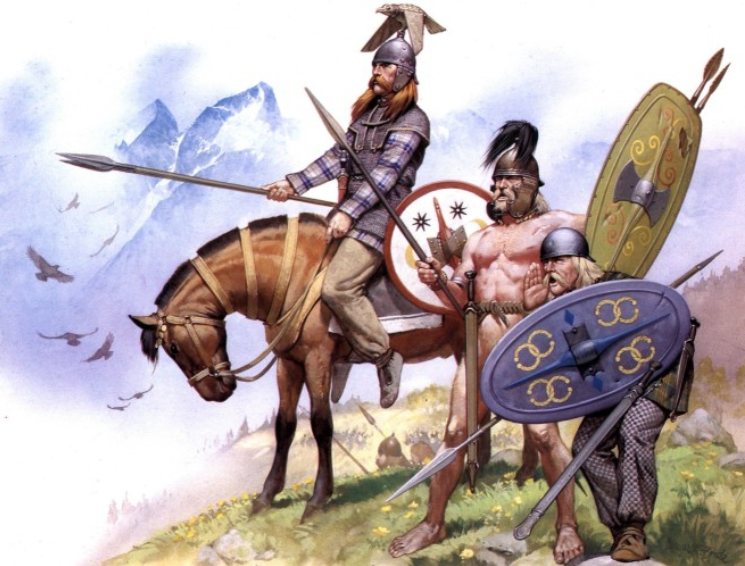

Golden Age of the Celts
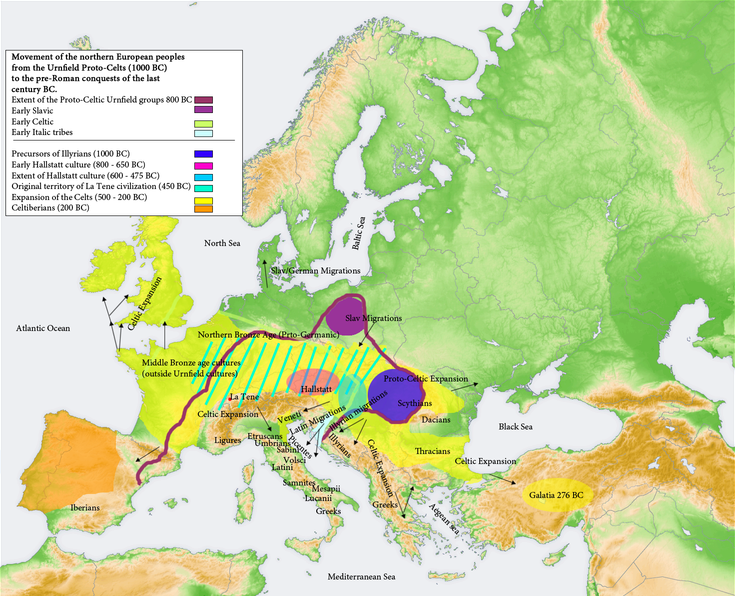
But we are anticipating, and must return to the period of the origins of Celtic history. As astronomers have discerned the existence of an unknown planet by the perturbations which it has caused in the courses of those already under direct observation, so we can discern in the fifth and fourth centuries before Christ the presence of a great power and of mighty movements going on behind a veil which will never be lifted now. This was the Golden Age of Celtdom in Continental Europe. During this period the Celts waged three great and successful wars, which had no little influence on the course of South European history. About 500 B.C. they conquered Spain from the Carthaginians. A century later we find them engaged in the conquest of Northern Italy from the Etruscans. They settled in large numbers in the territory afterwards known as Cisalpine Gaul, where many names, such as Mediolanum (Milan), Addua (Adda), Viro-dunum (Verduno), and perhaps Cremona (creamh, garlic), testify still to their occupation. They left a greater memorial in the chief of Latin poets, whose name, Vergil, appears to bear evidence of his Celtic ancestry. Towards the end of the fourth century they overran Pannonia, conquering the Illyrians.
Alliances with the Greeks
All these wars were undertaken in alliance with the Greeks, with whom the Celts were at this period on the friendliest terms. By the war with the Carthaginians the monopoly held by that people of the trade in tin with Britain and in silver with the miners of Spain was broken down, and the overland route across France to Britain, for the sake of which the Phocæans had in 600 B.C. created the port of Marseilles, was definitely secured to Greek trade. Greeks and Celts were at this period allied against Phœnicians and Persians. The defeat of Hamilcar by Gelon at Himera, in Sicily, took place in the same year as that of Xerxes at Salamis. The Carthaginian army in that expedition was made up of mercenaries from half a dozen different nations, but not a Celt is found in the Carthaginian ranks, and Celtic hostility must have counted for much in preventing the Carthaginians from lending help to the Persians for the overthrow of their common enemy. These facts show that Celtica played no small part in preserving the Greek type of civilisation from being overwhelmed by the despotisms of the East, and thus in keeping alive in Europe the priceless seed of freedom and humane culture.
Alexander the Great
When the counter-movement of Hellas against the East began under Alexander the Great we find the Celts again appearing as a factor of importance.
In the fourth century Macedon was attacked and almost obliterated by Thracian and Illyrian hordes. King Amyntas II was defeated and driven into exile. His son Perdiccas II was killed in battle. When Philip, a younger brother of Perdiccas, came to the obscure and tottering throne which he and his successors were to make the seat of a great empire he was powerfully aided in making head against the Illyrians by the conquests of the Celts in the valleys of the Danube and the Po. The alliance was continued, and rendered, perhaps, more formal in the days of Alexander. When about to undertake his conquest of Asia (334 B.C.) Alexander first made a compact with the Celts “who dwelt by the Ionian Gulf” in order to secure his Greek dominions from attack during his absence. The episode is related by Ptolemy Soter in his history of the wars of Alexander. It has a vividness which stamps it as a bit of authentic history, and another singular testimony to the truth of the narrative has been brought to light by de Jubainville. As the Celtic envoys, who are described as men of haughty bearing and great stature, their mission concluded, were drinking with the king, he asked them, it is said, what was the thing they, the Celts, most feared. The envoys replied: “We fear no man: there is but one thing that we fear, namely, that the sky should fall on us; but we regard nothing so much as the friendship of a man such as thou.” Alexander bade them farewell, and, turning to his nobles, whispered: “What a vainglorious people are these Celts!” Yet the answer, for all its Celtic bravura and flourish, was not without both dignity and courtesy. The reference to the falling of the sky seems to give a glimpse of some primitive belief or myth of which it is no longer possible to discover the meaning. The national oath by which the Celts bound themselves to the observance of their covenant with Alexander is remarkable. “If we observe not this engagement,” they said, “may the sky fall on us and crush us, may the earth gape and swallow us up, may the sea burst out and overwhelm us.” De Jubainville draws attention most appositely to a passage from the “Táin Bo Cuailgne,” in the Book of Leinster, where the Ulster heroes declare to their king, who wished to leave them in battle in order to meet an attack in another part of the field: “Heaven is above us, and earth beneath us, and the sea is round about us. Unless the sky shall fall with its showers of stars on the ground where we are camped, or unless the earth shall be rent by an earthquake, or unless the waves of the blue sea come over the forests of the living world, we shall not give ground.” This survival of a peculiar oath-formula for more than a thousand years, and its reappearance, after being first heard of among the Celts of Mid-Europe, in a mythical romance of Ireland, is certainly most curious, and, with other facts which we shall note hereafter, speaks strongly for the community and persistence of Celtic culture.
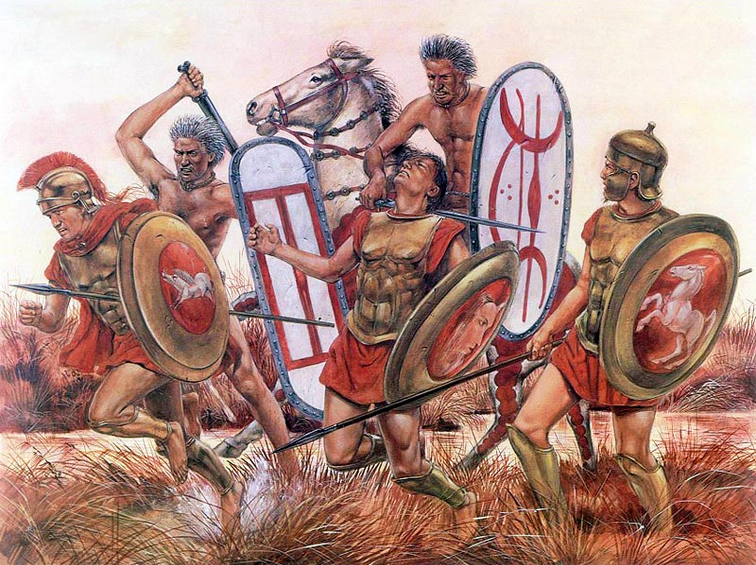

The Sack of Rome
We have mentioned two of the great wars of the Continental Celts; we come now to the third, that with the Etruscans, which ultimately brought them into conflict with the greatest power of pagan Europe, and led to their proudest feat of arms, the sack of Rome. About the year 400 B.C. the Celtic Empire seems to have reached the height of its power. Under a king named by Livy Ambicatus, who was probably the head of a dominant tribe in a military confederacy, like the German Emperor in the present day, the Celts seem to have been welded into a considerable degree of political unity, and to have followed a consistent policy. Attracted by the rich land of Northern Italy, they poured down through the passes of the Alps, and after hard fighting with the Etruscan inhabitants they maintained their ground there. At this time the Romans were pressing on the Etruscans from below, and Roman and Celt were acting in definite concert and alliance. But the Romans, despising perhaps the Northern barbarian warriors, had the rashness to play them false at the siege of Clusium, 391 B.C., a place which the Romans regarded as one of the bulwarks of Latium against the North. The Celts recognised Romans who had come to them in the sacred character of ambassadors fighting in the ranks of the enemy. The events which followed are, as they have come down to us, much mingled with legend, but there are certain touches of dramatic vividness in which the true character of the Celts appears distinctly recognisable. They applied, we are told, to Rome for satisfaction for the treachery of the envoys, who were three sons of Fabius Ambustus, the chief pontiff. The Romans refused to listen to the claim, and elected the Fabii military tribunes for the ensuing year. Then the Celts abandoned the siege of Clusium and marched straight on Rome. The army showed perfect discipline. There was no indiscriminate plundering and devastation, no city or fortress was assailed. “We are bound for Rome” was their cry to the guards upon the walls of the provincial towns, who watched the host in wonder and fear as it rolled steadily to the south. At last they reached the river Allia, a few miles from Rome, where the whole available force of the city was ranged to meet them. The battle took place on July 18, 390, that ill-omened dies Alliensis which long perpetuated in the Roman calendar the memory of the deepest shame the republic had ever known. The Celts turned the flank of the Roman army, and annihilated it in one tremendous charge. Three days later they were in Rome, and for nearly a year they remained masters of the city, or of its ruins, till a great fine had been exacted and full vengeance taken for the perfidy at Clusium. For nearly a century after the treaty thus concluded there was peace between the Celts and the Romans, and the breaking of that peace when certain Celtic tribes allied themselves with their old enemy, the Etruscans, in the third Samnite war was coincident with the breaking up of the Celtic Empire.
Two questions must now be considered before we can leave the historical part of this Introduction. First of all, what are the evidences for the widespread diffusion of Celtic power in Mid-Europe during this period? Secondly, where were the Germanic peoples, and what was their position in regard to the Celts?

Celtic Place-names in Europe
To answer these questions fully would take us (for the purposes of this volume) too deeply into philological discussions, which only the Celtic scholar can fully appreciate. The evidence will be found fully set forth in de Jubainville’s work, already frequently referred to. The study of European place-names forms the basis of the argument. Take the Celtic name Noviomagus composed of two Celtic words, the adjective meaning new, and magos (Irish magh) a field or plain. There were nine places of this name known in antiquity. Six were in France, among them the places now called Noyon, in Oise, Nijon, in Vosges, Nyons, in Drôme. Three outside of France were Nimègue, in Belgium, Neumagen, in the Rhineland, and one at Speyer, in the Palatinate.
The word dunum, so often traceable in Gaelic place-names in the present day (Dundalk, Dunrobin, &c.), and meaning fortress or castle, is another typically Celtic element in European place-names. It occurred very frequently in France—e.g., Lug-dunum (Lyons), Viro-dunum (Verdun). It is also found in Switzerland—e.g., Minno-dunum (Moudon), Eburo-dunum (Yverdon)—and in the Netherlands, where the famous city of Leyden goes back to a Celtic Lug-dunum. In Great Britain the Celtic term was often changed by simple translation into castra; thus Camulo-dunum became Colchester, Brano-dunum Brancaster. In Spain and Portugal eight names terminating in dunum are mentioned by classical writers. In Germany the modern names Kempton, Karnberg, Liegnitz, go back respectively to the Celtic forms Cambo-dunum, Carro-aunum, Lugi-dunum, and we find a Singi-dunum, now Belgrade, in Servia, a Novi-dunum, now Isaktscha, in Roumania, a Carro-dunum in South Russia, near the Dniester, and another in Croatia, now Pitsmeza. Sego-dunum, now Rodez, in France, turns up also in Bavaria (Wurzburg), and in England (Sege-dunum, now Wallsend, in Northumberland), and the first term, sego, is traceable in Segorbe (Sego-briga) in Spain. Briga is a Celtic word, the origin of the German burg, and equivalent in meaning to dunum.
One more example: the word magos, a plain, which is very frequent as an element of Irish place-names, is found abundantly in France, and outside of France, in countries no longer Celtic, it appears in Switzerland (Uro-magus now Promasens), in the Rhineland (Broco-magus, Brumath), in the Netherlands, as already noted (Nimègue), in Lombardy several times, and in Austria.
The examples given are by no means exhaustive, but they serve to indicate the wide diffusion of the Celts in Europe and their identity of language over their vast territory.
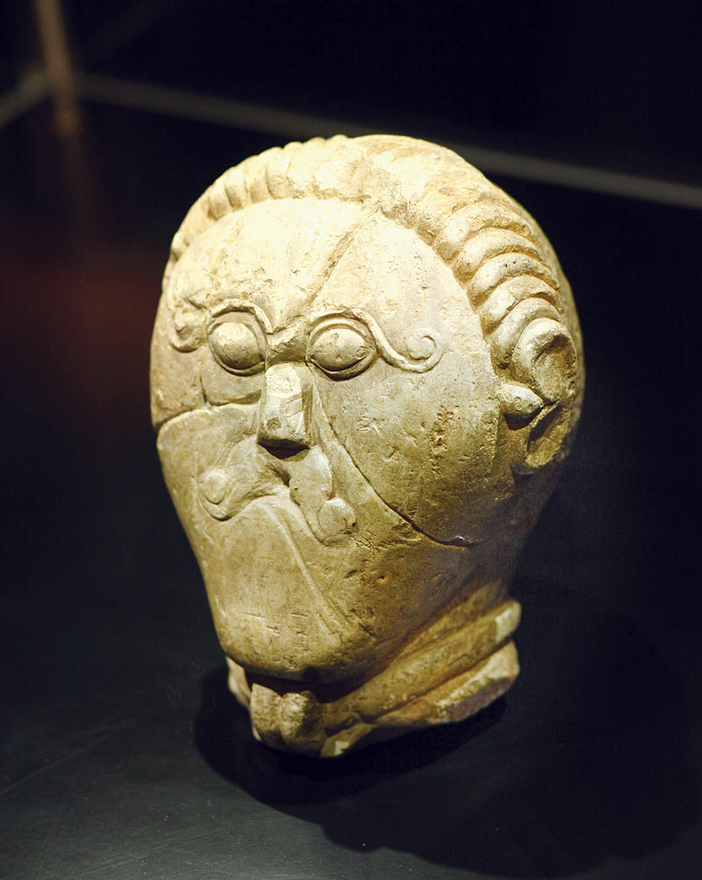

Early Celtic Art
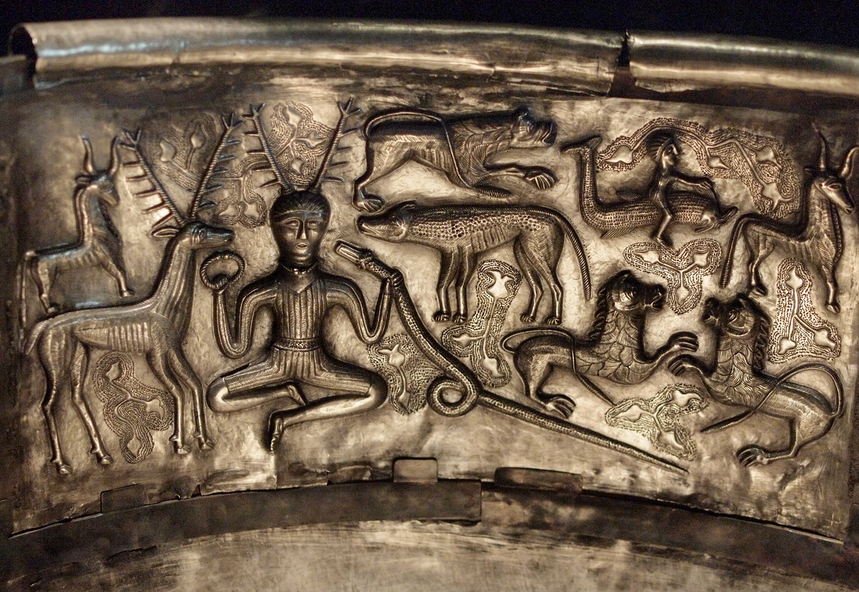
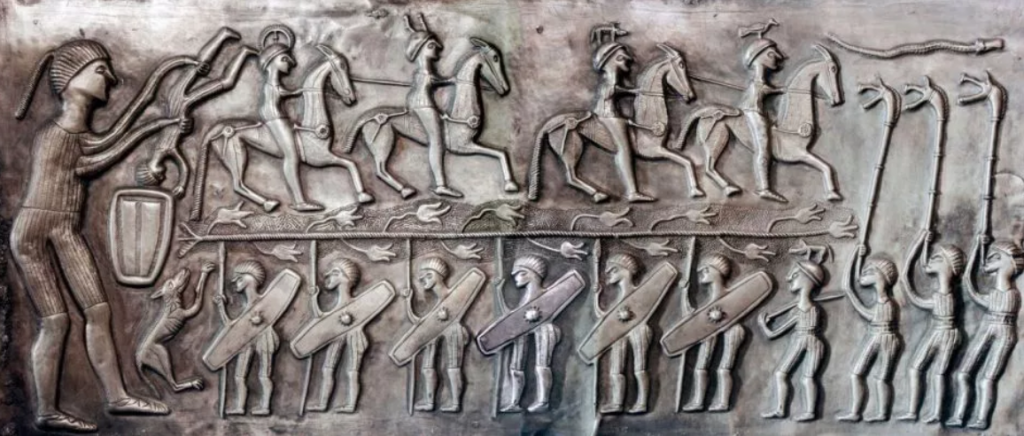
The relics of ancient Celtic art-work tell the same story. In the year 1846 a great pre-Roman necropolis was discovered at Hallstatt, near Salzburg, in Austria. It contains relics believed by Dr. Arthur Evans to date from about 750 to 400 B.C. These relics betoken in some cases a high standard of civilisation and considerable commerce. Amber from the Baltic is there, Phoenician glass, and gold-leaf of Oriental workmanship. Iron swords are found whose hilts and sheaths are richly decorated with gold, ivory, and amber.
The Celtic culture illustrated by the remains at Hallstatt developed later into what is called the La Tène culture. La Tène was a settlement at the north-eastern end of the Lake of Neuchâtel, and many objects of great interest have been found there since the site was first explored in 1858. These antiquities represent, according to Dr. Evans, the culminating period of Gaulish civilisation, and date from round about the third century B.C. The type of art here found must be judged in the light of an observation recently made by Mr. Romilly Allen in his “Celtic Art” (p. 13):
“The great difficulty in understanding the evolution of Celtic art lies in the fact that although the Celts never seem to have invented any new ideas, they possessed an extraordinary aptitude for picking up ideas from the different peoples with whom war or commerce brought them into contact. And once the Celt had borrowed an idea from his neighbours he was able to give it such a strong Celtic tinge that it soon became something so different from what it was originally as to be almost unrecognisable.”
Now what the Celt borrowed in the art-culture which on the Continent culminated in the La Tène relics were certain originally naturalistic motives for Greek ornaments, notably the palmette and the meander motives. But it was characteristic of the Celt that he avoided in his art all imitation of, or even approximation to, the natural forms of the plant and animal world. He reduced everything to pure decoration. What he enjoyed in decoration was the alternation of long sweeping curves and undulations with the concentrated energy of close-set spirals or bosses, and with these simple elements and with the suggestion of a few motives derived from Greek art he elaborated a most beautiful, subtle, and varied system of decoration, applied to weapons, ornaments, and to toilet and household appliances of all kinds, in gold, bronze, wood, and stone, and possibly, if we had the means of judging, to textile fabrics also. One beautiful feature in the decoration of metal-work seems to have entirely originated in Celtica. Enamelling was unknown to the classical nations till they learned from the Celts. So late as the third century A.D. it was still strange to the classical world, as we learn from the reference of Philostratus:
“They say that the barbarians who live in the ocean [Britons] pour these colours upon heated brass, and that they adhere, become hard as stone, and preserve the designs that are made upon them.”
Dr. J. Anderson writes in the “Proceedings of the Society of Antiquaries of Scotland”:
“The Gauls as well as the Britons—of the same Celtic stock—practised enamel-working before the Roman conquest. The enamel workshops of Bibracte, with their furnaces, crucibles, moulds, polishing-stones, and with the crude enamels in their various stages of preparation, have been recently excavated from the ruins of the city destroyed by Caesar and his legions. But the Bibracte enamels are the work of mere dabblers in the art, compared with the British examples. The home of the art was Britain, and the style of the pattern, as well as the association in which the objects decorated with it were found, demonstrated with certainty that it had reached its highest stage of indigenous development before it came in contact with the Roman culture.”
The National Museum in Dublin contains many superb examples of Irish decorative art in gold, bronze, and enamels, and the “strong Celtic tinge” of which Mr. Romilly Allen speaks is as clearly observable there as in the relics of Hallstatt or La Tène.
Everything, then, speaks of a community of culture, an identity of race-character, existing over the vast territory known to the ancient world as “Celtica.”
Celts and Germans
But, as we have said before, this territory was by no means inhabited by the Celt alone. In particular we have to ask, who and where were the Germans, the Teuto-Gothic tribes, who eventually took the place of the Celts as the great Northern menace to classical civilisation?
They are mentioned by Pytheas, the eminent Greek traveller and geographer, about 300 B.C., but they play no part in history till, under the name of Cimbri and Teutones, they descended on Italy to be vanquished by Marius at the close of the second century. The ancient Greek geographers prior to Pytheas know nothing of them, and assign all the territories now known as Germanic to various Celtic tribes.
The explanation given by de Jubainville, and based by him on various philological considerations, is that the Germans were a subject people, comparable to those “un-free tribes” who existed in Gaul and in ancient Ireland. They lived under the Celtic dominion, and had no independent political existence. De Jubainville finds that all the words connected with law and government and war which are common both to the Celtic and Teutonic languages were borrowed by the latter from the former. Chief among them are the words represented by the modern German Reich, empire, Amt, office, and the Gothic reiks, a king, all of which are of unquestioned Celtic origin. De Jubainville also numbers among loan words from Celtic the words Bann, an order; Frei, free; Geisel, a hostage; Erbe, an inheritance; Werth, value; Weih, sacred; Magus, a slave (Gothic); Wini, a wife (Old High German); Skalks, Schalk, a slave (Gothic); Hathu, battle (Old German); Helith, Held, a hero, from the same root as the word Celt; Heer, an army (Celtic choris); Sieg, victory; Beute, booty; Burg, a castle; and many others.
The etymological history of some of these words is interesting. Amt, for instance, that word of so much significance in modern German administration, goes back to an ancient Celtic ambhactos, which is compounded of the words ambi, about, and actos, a past participle derived from the Celtic root AG, meaning to act. Now ambi descends from the primitive Indo-European mbhi, where the initial m is a kind of vowel, afterwards represented in Sanscrit by a. This m vowel became n in those Germanic words which derive directly from the primitive Indo-European tongue. But the word which is now represented by amt appears in its earliest Germanic form as ambaht, thus making plain its descent from the Celtic ambhactos.
Again, the word frei is found in its earliest Germanic form as frijo-s, which comes from the primitive Indo-European prijo-s. The word here does not, however, mean free; it means beloved (Sanscrit priya-s). In the Celtic language, however, we find prijos dropping its initial p—a difficulty in pronouncing this letter was a marked feature in ancient Celtic; it changed j, according to a regular rule, into dd, and appears in modern Welsh as rhydd=free. The Indo-European meaning persists in the Germanic languages in the name of the love-goddess, Freia, and in the word Freund, friend, Friede, peace. The sense borne by the word in the sphere of civil right is traceable to a Celtic origin, and in that sense appears to have been a loan from Celtic.
The German Beute, booty, plunder, has had an instructive history. There was a Gaulish word bodi found in compounds such as the place-name Segobodium (Seveux), and various personal and tribal names, including Boudicca, better known to us as the “British warrior queen,” Boadicea. This word meant anciently “victory.” But the fruits of victory are spoil, and in this material sense the word was adopted in German, in French (butin) in Norse (byte), and the Welsh (budd). On the other hand, the word preserved its elevated significance in Irish. In the Irish translation of Chronicles xxix. 11, where the Vulgate original has “Tua est, Domine, magnificentia et potentia et gloria et victoria,” the word victoria is rendered by the Irish búaidh, and, as de Jubainville remarks, “ce n’est pas de butin qu’il s’agit.” He goes on to say: “Búaidh has preserved in Irish, thanks to a vigorous and persistent literary culture, the high meaning which it bore in the tongue of the Gaulish aristocracy. The material sense of the word was alone perceived by the lower classes of the population, and it is the tradition of this lower class which has been preserved in the German, the French, and the Cymric languages.”
Two things, however, the Celts either could not or would not impose on the subjugated German tribes—their language and their religion. In these two great factors of race-unity and pride lay the seeds of the ultimate German uprising and overthrow of the Celtic supremacy. The names of the German are different from those of the Celtic deities, their funeral customs, with which are associated the deepest religious conceptions of primitive races, are different. The Celts, or at least the dominant section of them, buried their dead, regarding the use of fire as a humiliation, to be inflicted on criminals, or upon slaves or prisoners in those terrible human sacrifices which are the greatest stain on their native culture. The Germans, on the other hand, burned their illustrious dead on pyres, like the early Greeks—if a pyre could not be afforded for the whole body, the noblest parts, such as the head and arms, were burned and the rest buried.










3.5
4.5