Editor’s note: The following is extracted from Ten Great Events in History, by James Johonnot (published 1887).
While the nobles and influential persons were thus preparing to co-operate, in case of a collision with the Spanish government, a sudden and disastrous movement occurred among the lower classes. It was stated and believed that the regent had given permission for the exercise of the Protestant form of worship, and throughout Flanders multitudes poured into the fields after the preachers. The reaction after the suppression of the previous years was very great, and the pent-up emotions were easily kindled into rage against the Catholics. Led on by fanatics, the ignorant masses made a concerted attack upon the Catholic churches, shattering their windows, tearing up their pavements, and destroying all the objects of art which they contained. The cathedral at Antwerp was the special object of attack, and it was reduced to an almost hopeless ruin. The patriot nobles exerted their influence, and at last succeeded in suppressing the violence and in restoring order.
![]()
Before the news of this outburst had reached Spain, Philip had resolved to crush the confederacy and break the proud spirit of the Netherlands. Secret orders were given for the collection of troops, the regent was instructed to amuse the patriots until the means of punishing them were ready, and in a short time it was hoped that there would no longer be a patriot or a heretic in the Low Countries. It is easy to conceive with what rage and bitterness of heart Philip, while indulging these dreams, must have received intelligence of the terrible doings of the iconoclasts. But, as cautious and dissimulating as he was obstinate and revengeful, he concealed his intentions in the meantime, announced them to the regent only in secret letters and dispatches, and held out hopes in public to the patriots and people of the Netherlands that he was soon to pay them a visit in person to inquire into the condition of affairs.
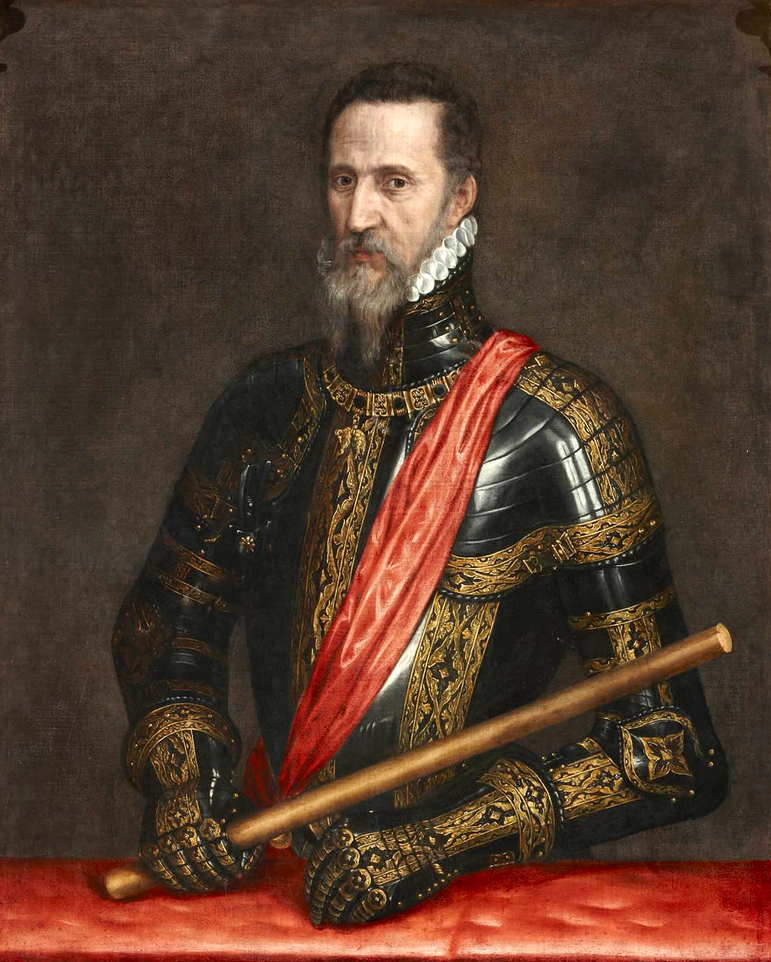

William had secret intelligence of the purpose of Philip in time to avert its worst consequences. The man whom Philip sent into the Netherlands at the head of the army, as a fit instrument of his purpose of vengeance, was the Duke of Alva, a personage who united the most consummate military skill with the disposition of a ruffian, ready to undertake any enterprise however base. Such was the man who, at the age of sixty, in the month of August, 1567, made his entry into the Netherlands at the head of an army of fifteen thousand men. One of his first acts was the arrest of the Counts Egmont and Horn. The regent resigned, and Alva was left in supreme control. Now ensued the grand struggle in the Netherlands. On the one hand was a nation of quiet, orderly people, industrious in a high degree, prosperous in their commerce, and disposed to remain peaceful subjects to a foreign monarch; on the other hand was a sovereign who, unthankful for the blessing of reigning over such a happy and well-disposed nation, and stimulated by passion and bigotry, resolved on compelling all to submit to his will on penalty of death.
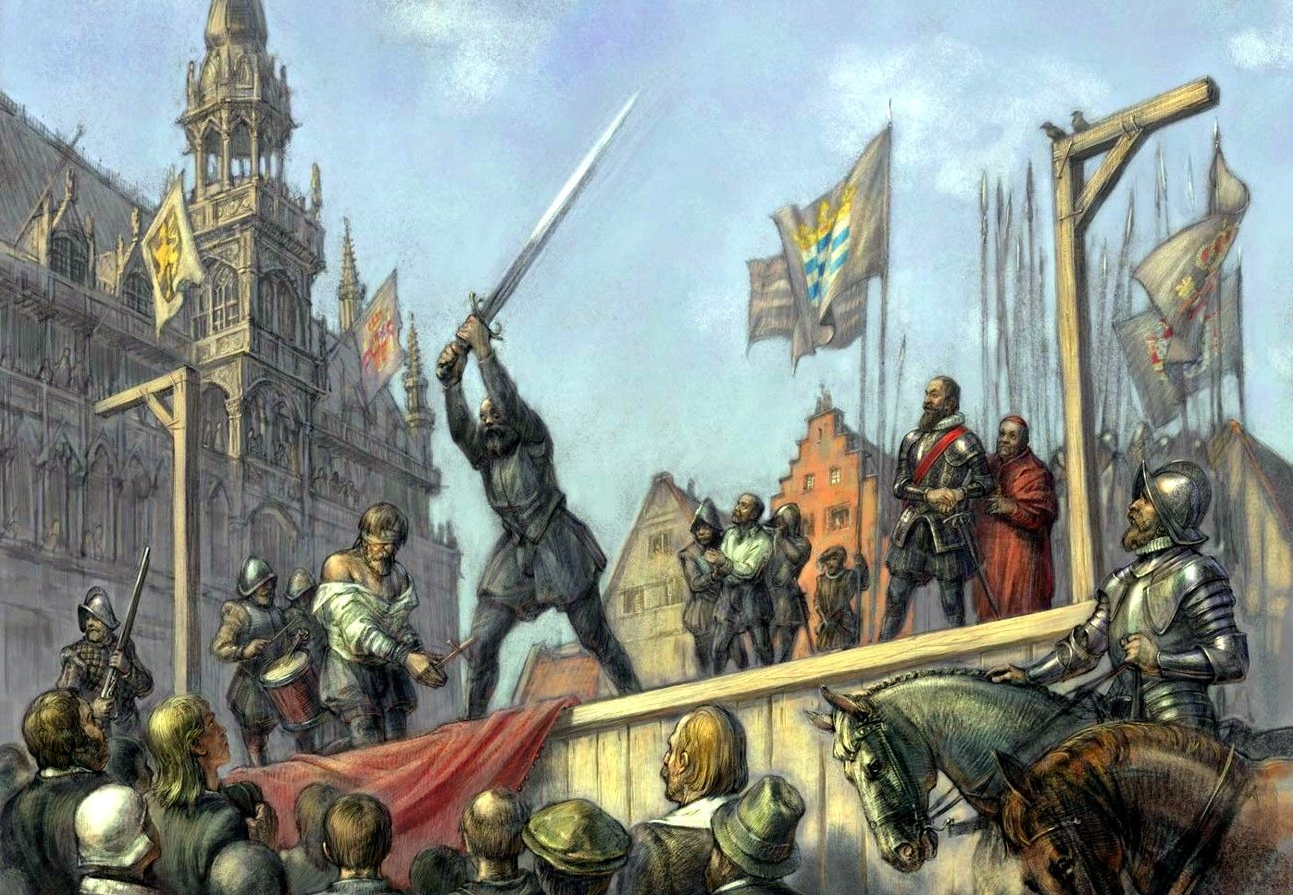

Alva at once commenced his persecutions. Supported by his army, blood was shed like water. The Inquisition was established, and began its work of unspeakable horrors in the Netherlands. Patriots and Protestants in crowds left the country. The leading men of the Netherlands were arrested and executed. Under circumstances of extreme ferocity Counts Egmont and Horn were beheaded at Brussels. Overwhelming taxes were imposed upon the people, and during the short period of his administration Alva executed eighteen thousand patriots, including many Catholics; for, in his rage against the free spirit of the Netherlanders, he recognized no distinction in condition or in religious belief.
In the meantime the Prince of Orange was active in devising means to liberate his unfortunate country from the terrible scourge to which it was subjected. For five years he battled incessantly against the Spanish power. Now he entered into combination with the English and now with the French, with the vain hope of obtaining a sufficient force to drive the Spaniards out of the country. Twice he raised an army and marched to the aid of the brave burghers, who still maintained their independence, and both times was defeated by the superior force and generalship of Alva. He organized a fleet which ravaged the coast, captured vessels laden with provisions for Alva’s army, and defended the ports within reach of their guns, When the shattered remains of William’s last army retreated across the German frontier, it seemed that the people of the Netherlands were about to be left to their fate.
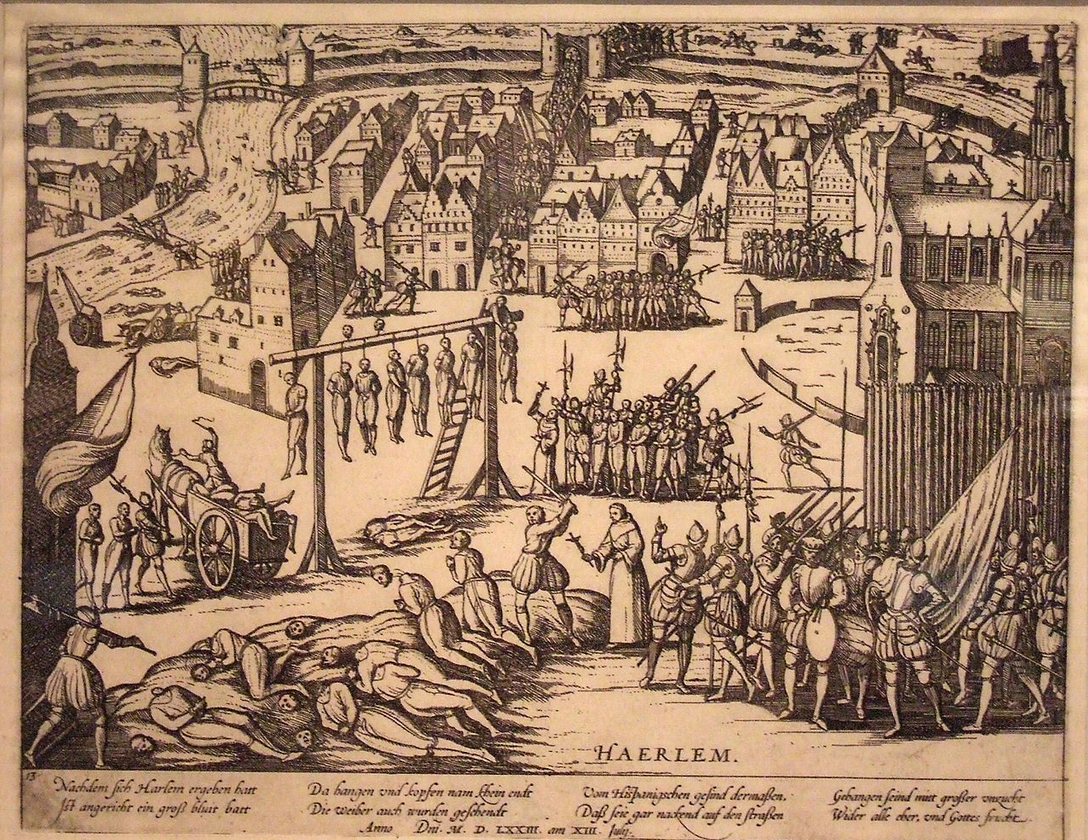

But sixty cities and towns were now in revolt, and, unless they were recovered, Philip could no longer be considered the king of the Netherlands. Nothing was left but the slow process of siege operations. Haarlem held out seven months, and cost the Spaniards ten thousand men. It surrendered at last under the promise of an amnesty to its defenders, when they were murdered by thousands in cold blood. But Philip was dissatisfied with Alva for his slow progress, and for his execution of Catholics as well as Protestants; and in 1753, after five years’ rule, he recalled him, and, with characteristic ingratitude, neglected and ill-treated him for his faithful but bloody services.

Don Luis Requesens succeeded the Duke of Alva as governor of the Netherlands and as commander of the Spanish army. While a zealous Catholic, he seems to have been a much more humane and just man than Alva. He began his administration by abolishing the most obnoxious measures of his predecessor, thus changing the whole tone of the government. Had he been left to follow his own counsels in everything, he doubtless would have come to an understanding with the Prince of Orange, and established peace upon a permanent basis. But the king was obstinately determined to capture the revolted cities and punish his rebel subjects, and the general was obliged to continue the war. At this time William was besieging Middleburg, on the island of Zealand, and one of the first acts of the newly-appointed, governor was to raise the siege. To this end he caused a large fleet to be assembled, and under the command of two experienced admirals he sent it down the Scheldt to the relief of Middleburg. The Prince of Orange immediately hastened to the critical spot, and gave direction to patriot operations. The Holland ships were collected, and a great naval battle took place on January 29, 1574. Although their force was much the greater, the Spaniards had little chance upon the water in a contest with the half-amphibious inhabitants of the Low Countries. The smaller vessels of the Prince of Orange fell upon the Spanish fleet with a ferocity which they could not withstand, and the result was a complete victory, with the destruction of their principal vessels. Middleburg soon after surrendered to the patriots, and the sway of William over the maritime provinces was rendered complete.